There are a number of ways to find the probability of more than one event.
Some of them work really well if you have a small number of events, but can be a pain if you have a large amount of data.
What is a two-way table?
A two-way table is a table with two outcomes (one along the top and one down the side), with the total outcomes classified in the cells in the middle.
It's really useful if you have a large amount of data and want to sort it by two classes.
Example 1:
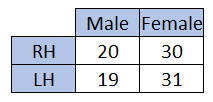
The two-way table below shows 100 students classified by their gender, and whether they are right-handed or left-handed.
The first step is to ensure that we know what this actually means.
The number 20 in the top left cell tells us there are 20 right-handed males.
The number 31 in the bottom right cell tells us there are 31 left-handed females.
Adding up all the numbers in the grid, will tell us the total outcomes for finding the probabilities.
Note: don't add any numbers that are in the title bits - the bits in blue.
Example 2:
For the two-way table shown, I pick a student at random.
Find the probability that the student is...
a) A right-handed male
There are 20 right-handed males and 100 people in total.
This is a probability of 20/100 which cancels to 1/5
b) Female
There are 61 females in this and 100 people in total
This is a probability of 61/100
c) A left-handed girl
There are 31 left-handed girls out of the 100 in total.
This is a probability of 31/100
Let's have a go at some questions now.