Did you know the smallest muscle in the human body is only 1 mm long?! It's called the stapedius muscle and found in the ear.
The muscles and bones in the body interact with one another to allow movement. This is known as biomechanics.
.jpg)
Muscle cells are specialised cells and they work together to form muscle tissue. Muscles work really hard and in order to do their job they have certain adaptations, for example they have lots of mitochondria. Mitochondria is an organelle where energy is produced from respiration. Muscles also have a good supply of blood. Blood carries oxygen which is also needed for respiration, along with glucose from our food to produce energy.
Why do muscles need so much energy? So they can contract (shorten/tighten). This allows them to pull on bones to allow movement.
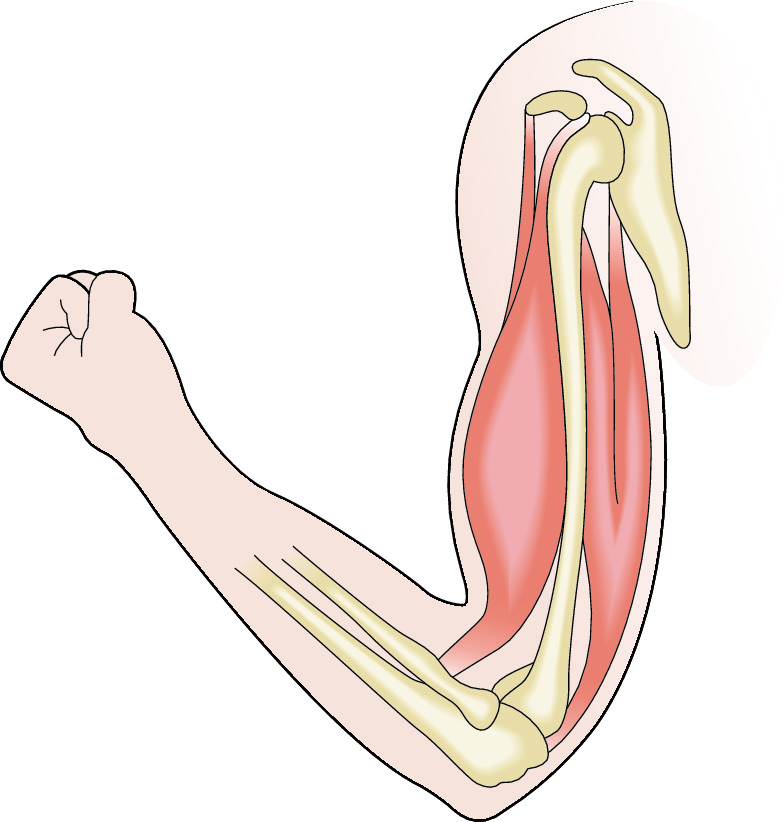
So what type of muscles are there?
There are three main groups of muscle:

1. Skeletal muscle - this is the main group of muscle found in the body. Tendons attach muscles to the bone, these muscles allow us to move. We can see from the image above that when a muscle contracts it gets shorter and thicker and ends up pulling on a tendon which pulls on the bone it's attached to, making it move. A force is produced by the muscle (you may remember from your physics lessons that forces are measured in Newtons).
2. Cardiac muscle - found in our heart and helps to pump blood around the body.
3. Smooth muscle - controls involuntary movement like in our stomach and intestines, helping our food to pass along our digestive system.
In this activity, we're going to look at the different type of muscles and their functions.







