By now we should know that all living things are made of cells, and that groups of cells make up a tissue and that groups of tissues make up organs. You may have even looked at different organ systems in the human body, like the digestive system. Well, these groups of cells, tissues and organs are found in plants as well. The main one that we all know, because it is the most obvious, is the plant organs such as the leaf.
How do plants and humans differ?
Plants have a different set of tissues:
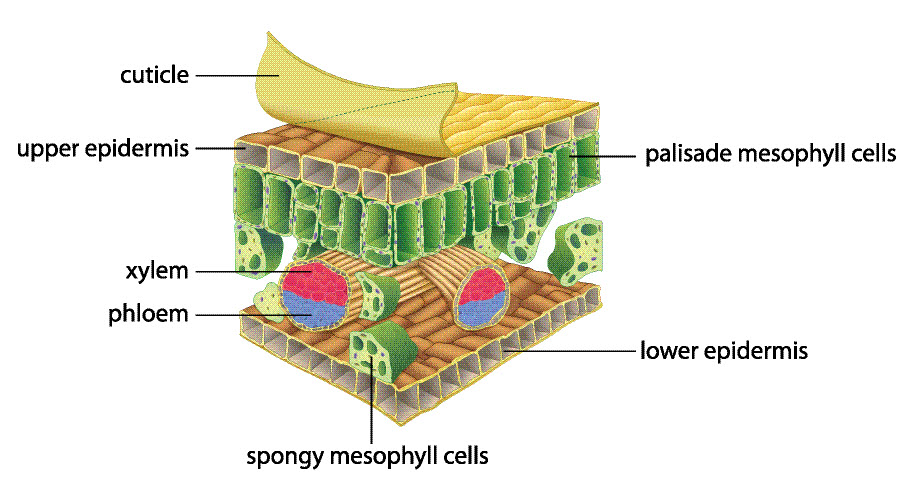
Epidermal - which covers the plant and does a similar job to our skin.
Mesophyll - responsible for photosynthesis (there are two types!).
Xylem and phloem - which carry food and water through the plant.
Let’s look at these in more detail now:
The epidermal tissues surround the plant and stop it from getting harmed by pathogens (bacteria, viruses and fungus). They also prevent harm from other things, like caterpillars – some epidermal tissues are even poisonous (like rhubarb leaves), or contain hairs that sting (like stinging nettles).
Next, we have the mesophyll. This is where most of the photosynthesis happens. Can you remember what photosynthesis needs for it to happen? It needs light, water and carbon dioxide. So, at the top of the leaf there are a load of photosynthesis cells that look like a fence to make the most of the sunlight. We call this the palisade mesophyll (palisade...like a fence).
Underneath this, we have the spongy mesophyll. Remember, in order to be able to photosynthsise a plant needs carbon dioxide. Well, that carbon dioxide needs to get to the palisade mesophyll, and it does this through the spongy mesophyll. There are loads of air pockets in order to get that carbon dioxide in and get rid of the oxygen.
Stomata (small openings) let carbon dioxide diffuse into the leaf for photosynthesis and let water out into the atmosphere. They can open and close – it’s pretty amazing!
That leaves us with the xylem and phloem. The xylem are responsible for moving water through a plant by a process called transpiration. This is just like a plant's version of sucking on a straw. Plants let water out of their leaves and that, in turn, sucks water up from the roots so it can reach the leaves and be used in photosynthesis. The phloem move sugars and minerals around the plant in a process that is called translocation. I know they sound similar but it is important that you know the difference - it is a popular question for most exam boards.
So that’s the leaf – now take a look at the image and get to know it before you try the questions!