Diamond and graphite are made of the same atoms, but their properties are totally different! How does this work?
Both diamond and graphite have giant structures made of pure carbon, but they have different patterns of bonds between the carbon atoms.

The reason that diamonds are good jewels is that they are so hard. This means that they don't get scratched, so they stay shiny.
(1)(1).png)
The structure of diamond is a giant covalent structure. Every carbon is linked to four other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. All the bonds in the diamond structure are covalent, so every single bond is very strong - there are no weak links in the structure. There are no free electrons or ions, so diamond cannot conduct electricity.
Graphite is also made of carbon, but the arrangement of the atoms is very different:
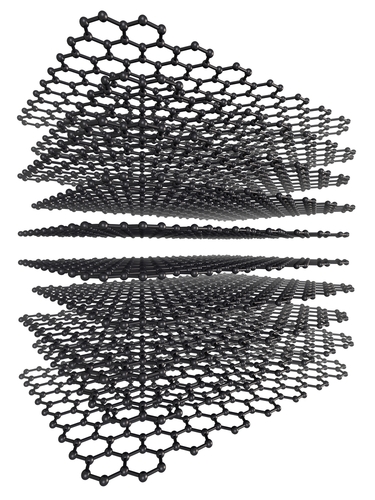
This picture shows the graphite structure. There are hexagonal rings of carbon atoms, which link together to make sheets. The bonds in the sheets are covalent, so each sheet is very strong. The bonds holding the layers together are much weaker. This means that the layers can slide over each other easily. When you write with a pencil, the 'lead' in the middle is actually graphite. As you write, flakes of graphite are broken off the pencil lead and stick to the paper.

The other important difference between diamond and graphite is that graphite conducts electricity, unlike diamond. Each carbon atom in graphite makes three covalent bonds in the layer. That means there is a spare, delocalised bond which sits between the layers. These can move, which allows graphite to conduct electricity.
Even though diamond and graphite are both made of carbon atoms, the way the atoms are joined together is important in explaining why diamond and graphite behave in they ways they do.
Properties of diamond and graphite
You don't need to learn these properties by heart, but you might be asked to draw conclusions and explain patterns:
| Property | Diamond | Graphite (along layers) | Graphite (perpendicular to layers) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 3.5 | 2.1 | * |
| Absolute hardness | 1500 | 0.5 | 400 |
| Electrical conductivity | 10-12 | 250 000 | 300 |
| Stiffness | 100 | 1000 | 35 |
* density is mass divided by volume, so it doesn't vary with direction
For example, you could be asked: "How many times harder is diamond than the maximum hardness of graphite? Explain the difference."
Look in the table: Hardness of diamond = 1500, maximum hardness of graphite = 400
Write a word equation: Ratio = hardness of diamond ÷ hardness of graphite
Substitute numbers: Ratio = 1500 ÷ 400 = 3.75
Diamond is 3.75 times harder than graphite in its hardest direction.
Link the different properties to the structure: Even in its hardest direction, graphite is weakened by the layered structure. Diamond has no weak directions.
Diamond and graphite are a great example of structure-property relationships.
The key ideas are that diamond is equally strongly bonded in all directions. Graphite has strong layers, but weaker links (with electrical conduction) in the gaps between the layers.
Let's move on to some questions now.








