An electric current can be used to separate compounds into their different elements, and also to create new products using a method called electrolysis. The diagram below shows an electrolytic cell while electrolysis of sodium chloride (NaCl) is taking place:
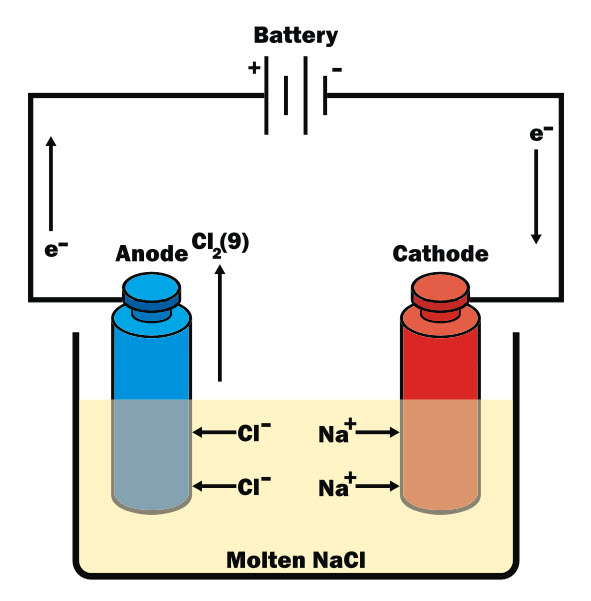
The principle is that the electric current separates the compound into its ions. Ions are atoms that have gained or lost one or more electrons in order to make the compound with the other element(s). The electrodes used for electrolysis are a positive one (anode), which attracts negative ions (anions), and a negative one (cathode), which attracts positive ions (cations).
The electrolyte is the molten compound or the solution that is separated during electrolysis, and it must be able to conduct electricity.
Electrolysis of dilute sulfuric acid
Hydrogen is made at the cathode: 2H+ + 2e- 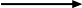 H2. The positive hydrogen ions migrate towards the negative cathode, gain one electron each and are discharged as hydrogen gas.
H2. The positive hydrogen ions migrate towards the negative cathode, gain one electron each and are discharged as hydrogen gas.
Oxygen is made at the anode: 4OH- - 4e- 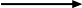 2H2O + O2. The negative hydroxyl ions migrate towards the positive anode, they lose one electron each and combine to form water and oxygen.
2H2O + O2. The negative hydroxyl ions migrate towards the positive anode, they lose one electron each and combine to form water and oxygen.
Purifying copper
Electrolysis is also used to purify metals, such as copper. Copper is extracted as an ore (compounds of copper with other elements) and is purified with this method. The anode is the impure copper; it dissolves into the electrolyte, and pure copper coats the cathode. This is called electroplating.
Let's have a go at some questions now.








