Fantastic effort! You have decided to spend some valuable time practising for your maths SATs test.
In this activity, we will look at how to find the missing angle in a shape or around a point.
How do we find missing angles on a straight line?
The angles on a straight line add up to 180°.
To calculate the missing angle on a straight line, take away the known angle from 180°.
.png)
180° - 65° = 115°
How do we find missing angles in a full turn?
The angles in a full turn up add up to 360°.
To calculate the missing angle in a full turn, take away the known angle from 360°.
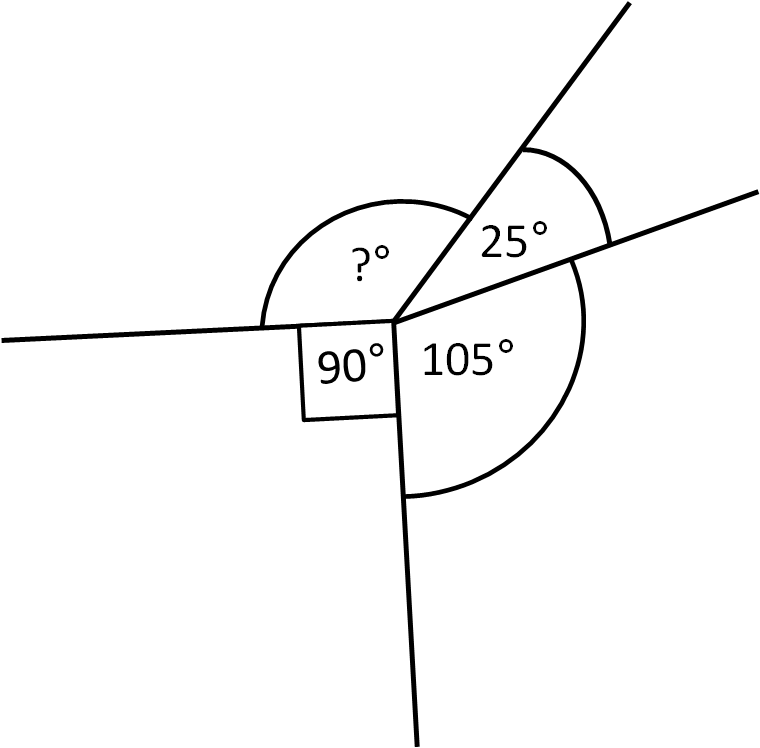
105° + 90° + 25° = 220°
360° - 220° = 140°
How do we find missing angles on intersecting lines?
All four angles will add up to 360°.
Opposite angles on a cross are equal.
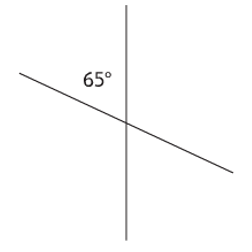
Step 1 (we know the angle opposite 65° is also worth 65° so add these together): 65° + 65° =130°
Step 2 (subtract the total of these two angles from 360°): 360° - 130° = 230°.
Step 3 (Divide this total by 2 to find what each of the two remaining angles is worth): 230°÷ 2 =115°
How do we find missing angles in a triangle?
The angles in a triangle always add up to 180°.
To find the missing angle, add together the known angles and subtract from 180°.

If you are given a triangle like this, but asked to find the missing angle, focus only on the angles given, ignore the other information.
57° + 90° = 147°
180° - 147° = 33°
How do we find missing angles in a quadrilateral?
A quadrilateral is a shape with four straight sides, like a square, rhombus, parallelogram, trapezium, rectangle.
The angles in a quadrilateral will add always add up to 360°
To find the missing angle, add together the known angles and then subtract from 360°

90° + 90° + 40° = 220°
360° - 220° = 140
Now we have revised those key facts, time to have a go at some practice questions!
Good luck!








