Some compounds decompose or break down when they are heated to sufficiently high temperatures.
These reactions are called thermal decomposition reactions.
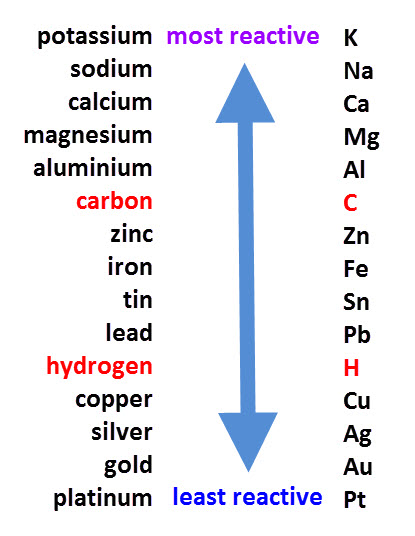
Carbonates of metals from the lower half of the reactivity series tend to decompose on heating to produce a metal oxide and carbon dioxide gas. But metals such as potassium and sodium, at the top of the reactivity series, are the most stable and will not normally decompose with heat.
The word equation for those metal carbonates that do thermally decompose is:
metal carbonate → metal oxide + carbon dioxide
eg. When calcium carbonate, a green powder, is heated it thermally decomposes into copper oxide (a black powder) and carbon dioxide gas.
Calcium carbonate → Calcium oxide + carbon dioxide
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Most metal hydroxides will undergo thermal decomposition, and the word equation is:
metal hydroxide → metal oxide + water
eg. Sodium hydroxide will decompose on heating to produce sodium oxide and water.
Sodium hydroxide → Sodium oxide + water
2NaOH → Na2OH + H2O
Hopefully, you have noticed from the two examples above, that in a thermal decomposition reaction, there is only ever one reactant and there are always two or more products.

Ready to try some questions now?








