The leaves of a plant are exceptionally important when it comes to photosynthesis. They are like factories that produce the food that plants need to grow and survive. But how?
Leaves are designed and adapted to allow photosynthesis to take place. They are flat and broad to capture as much of the light energy from the Sun as possible.
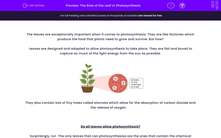
They also contain lots of tiny holes called stomata which allow for the absorption of carbon dioxide and the release of oxygen.
Do all leaves allow photosynthesis?
Surprisingly, no! The only leaves that can photosynthesise are the ones that contain the chemical chlorophyll. So how do you know what leaves contain chlorophyll? Easy, chlorophyll is the green pigment in leaves, so if a leaf is green, it will photosynthesise.

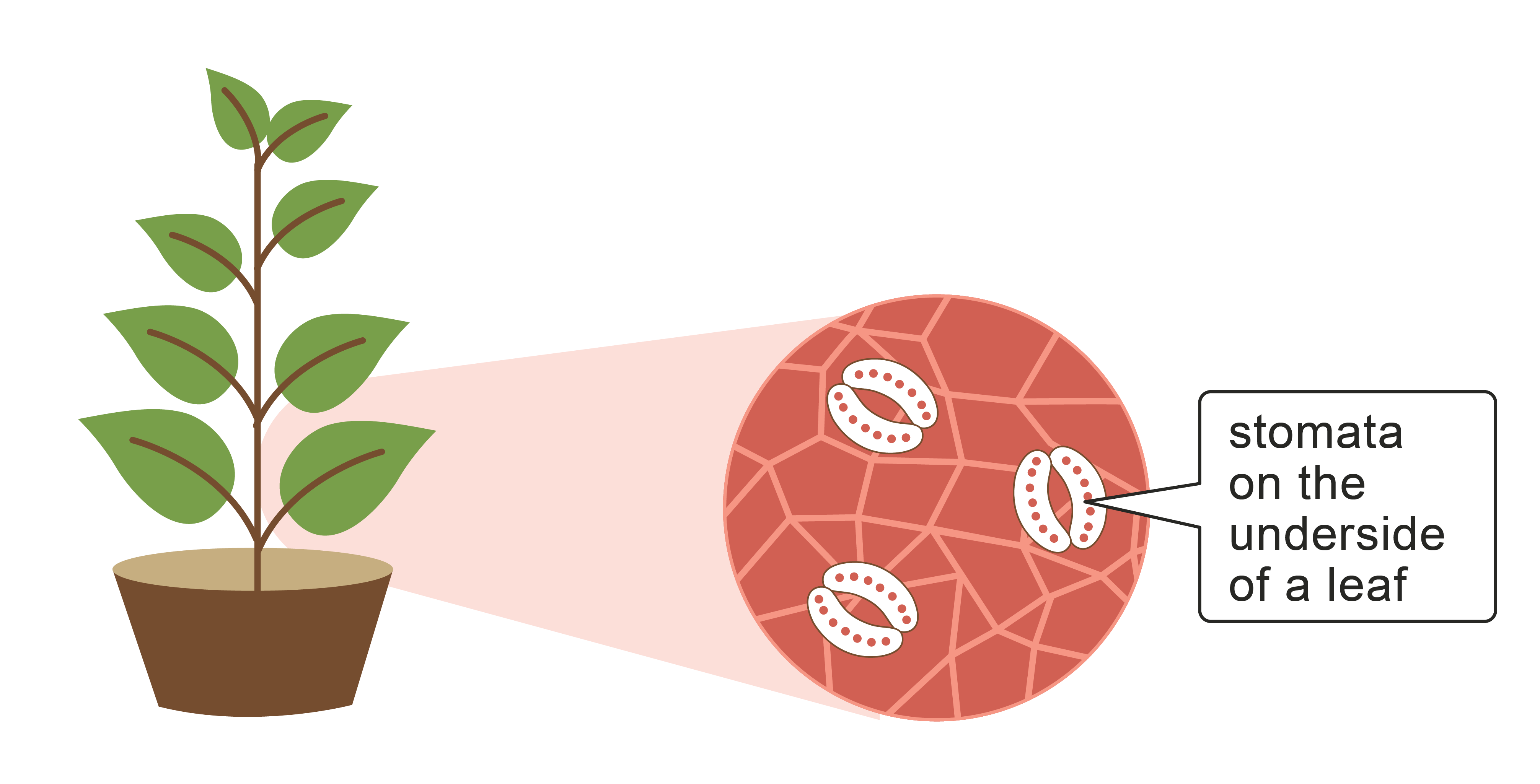
Chlorophyll is the chemical responsible for converting light energy from the Sun into chemical energy. This chemical energy is then used to make glucose (C6H12O6) from carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
Light energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O ![]() C6H12O6 + 6O2
C6H12O6 + 6O2
What happens to the glucose?
The glucose produced in photosynthesis has a variety of uses. Some of the glucose is used to create other chemicals needed in the plant such as proteins. Some is converted into starch and stored in the plant for later use and some is used for respiration.
Respiration
Respiration is the process that all living organisms use to get the energy they need. Plants use the glucose produced in photosynthesis and convert it into the energy needed for the living processes in green plants:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ![]() 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
Experiment - Testing a leaf for starch
A simple experiment can be done to prove that green plants photosynthesise:
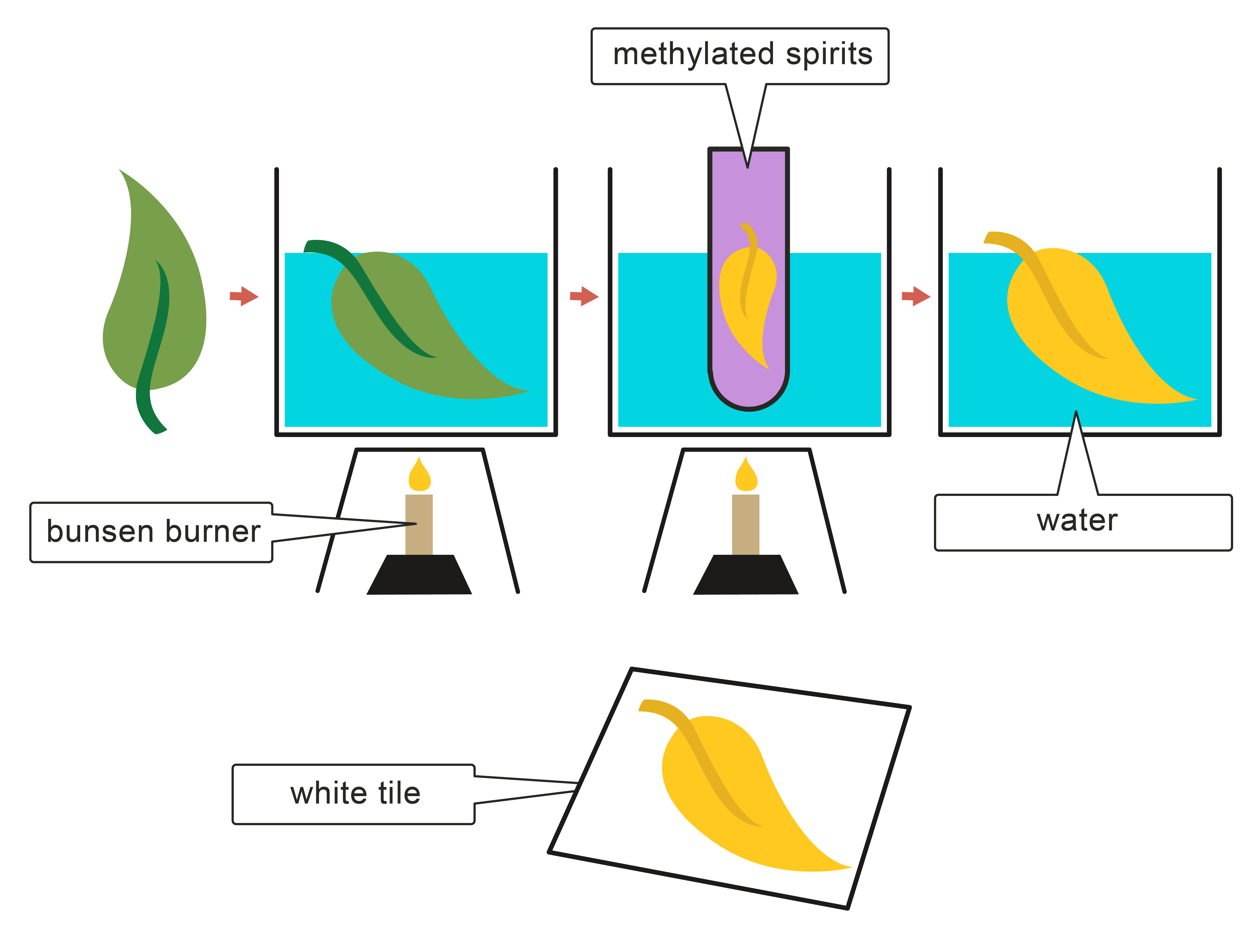
Step 1: Boil the leaf in water for around 10 minutes to soften the leaf.
Step 2: Place the leaf in a boiling tube containing methylated spirit (or ethanol) and heat for a further 10 minutes to remove the chlorophyll from the leaf.
Important: Make sure the Bunsen burner is switched off before using the methylated spirit as it is highly flammable.
Step 3: Rinse the leaf with cold water.
Step 4: Test the leaf with iodine. If the plant has photosynthesised, the iodine should turn from brown to blue/black, indicating the presence of starch.
The white of a variegated leaf does not contain any chlorophyll. What would you expect to see happen when this type of leaf is tested for starch?

We will now answer some more questions on photosynthesis and the importance of leaves.