What is kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy is associated with movement. The more kinetic energy you have, the faster and further you move.

A sports car has a lot of kinetic energy (when it is moving at top speed).
The same applies to particles. The more kinetic energy a particle has, the faster it moves!
How does this relate to heat?
Heat (which is a store of thermal energy) flows in a substance because particles collide (bump into each other) and transfer the thermal energy to one another. Thermal energy changes to kinetic energy, which makes particles move even faster. The transfer of heat in this way is called conduction. In this way, all the particles in an object eventually reach thermal equilibrium, which means that all the particles are at the same temperature and so vibrating (moving) at the same speed.

Conduction is the relationship between heating and movement of the particles. Collisions occur when particles bump into each other as they vibrate or move.
What is temperature?
Temperature is effectively a measure of the average speed of the particles in a substance. We measure it in degrees Celsius. The greater the temperature of a substance, the faster its particles must be moving, and therefore, the greater the average kinetic energy of its particles.
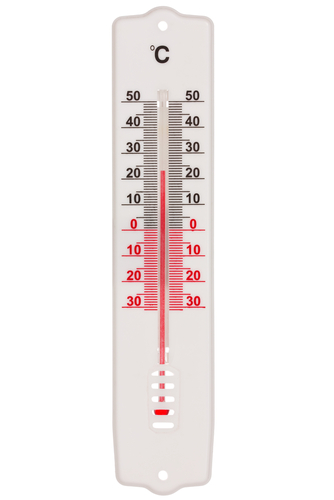
When materials gain thermal energy (heat), their temperature increases, and they also expand because their particles have more kinetic energy to move further apart. On the other hand, when the temperature drops, materials contract ('shrink'). If you imagine putting fluid into a thin tube, it would expand and climb higher up the tube at high temperatures, while shrinking and falling lower into the tube at lower temperatures. This is how a thermometer works.
See if you can test your knowledge with the following questions...








