.jpg)
Why can you smell someone's stinky PE socks from all the way across the classroom? Yuk! Normally it's because sweat and other molecules are moving away from the socks and spread out in the air. This is called diffusion.
Diffusion is the spreading out of the particles of any substance in a solution, or particles of a gas, resulting in movement from an area of higher concentration (where there's more particles in a certain solution or area) to an area of lower concentration (where there are fewer particles).
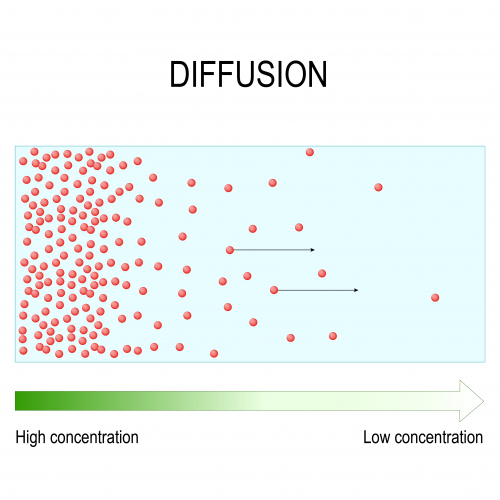
Living organisms need different substances to be able to survive and function. These substances need to be transported into and out of their cells through diffusion (as well as osmosis and active transport - you will learn more about these later!). During diffusion, molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. They are said to move down a concentration gradient. Particles diffuse until they are evenly spaced apart. Diffusion is a passive process which means that no energy is needed and it happens naturally.
Diffusion in organisms
The surface area to volume ratio of an organism means how much area an organism has in comparison to its volume. As organisms get larger, their surface area to volume ratio gets smaller, for example, an elephant has a smaller surface area to volume ratio than a mouse!
Breathing involves exchanging gases in the lungs - this requires diffusion. When you breathe in, oxygen in the inhaled air diffuses through the tiny alveoli (air sacs) in your lungs into your bloodstream. The oxygen is transported around your body. Carbon dioxide is the waste gas produced by respiration. Carbon dioxide diffuses from cells into the bloodstream and is exhaled by the lungs.

The alveoli have a few adaptations that make gas exchange very efficient. They are only one cell thick making them very thin, which allows gases to pass through easily and quickly. They also have a large combined surface area, allowing large amounts of gases to be exchanged with each breath.
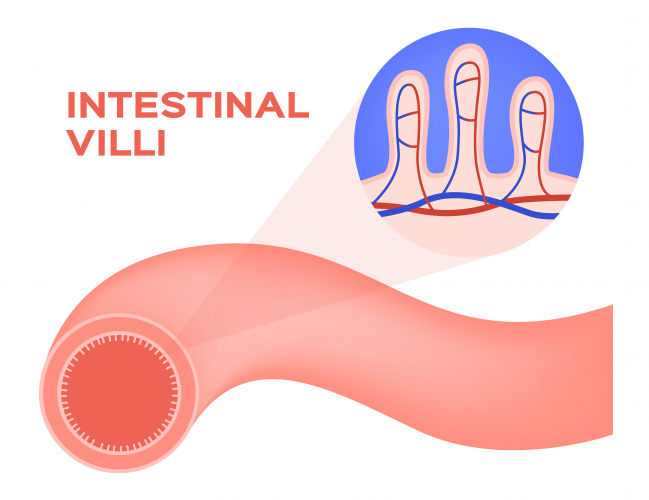
Another example of diffusion is in the small intestine. Digested food is broken down into small molecules such as glucose and amino acids. These important molecules need to be transported around the body via the blood. The small intestine is lined with many finger-like projections called villi. The molecules diffuse through the villi of the small intestine into the blood to be transported around the body. The villi are well adapted for this function, being very thin and having finger-like projections that increase the surface area. Villi also have partially permeable membranes. This means the membrane has pores that allow smaller molecules through but not larger molecules.
.jpg)
Diffusion also occurs in plants. Plants take in carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and produce oxygen. These enter and leave the plant through the process of diffusion. The structure of the leaf is adapted for gas exchange. There are tiny pores, called stomata, in the surface of the leaf. There are usually more stomata on the underside of a leaf than on the topside. The stomata allow carbon dioxide to enter the leaf for photosynthesis. Molecules of carbon dioxide diffuse from a region of higher concentration (the atmosphere) to a lower concentrated area (leaf). The stomata also allow oxygen to diffuse out.
Factors affecting diffusion
Different factors can affect diffusion and how quickly it happens. Some of these factors are:
The difference in concentrations (concentration gradient) - having a large difference in concentrations means that diffusion can occur at a quicker rate, as particles will naturally move from a high to low concentration.
The temperature - the higher the temperature, the more energy the particles will have to move and spread out.
The surface area of the membrane - the larger the surface area, the faster the rate of diffusion. This is because more particles can pass through the membrane as there is more area, as in the alveoli in the lungs.
A thin membrane - to provide a short diffusion path
In the following activity, you will explain the process of diffusion.








