By reacting metals with oxygen, acids and water, scientists have been able to construct a table of metals, listing them in order from the most to the least reactive.
This table is called the reactivity series:
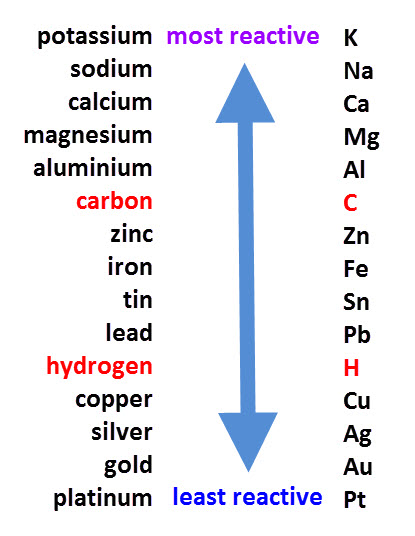
The metals at the top are so reactive that they can even set on fire or explode when stored in water. They also tarnish (go dull) very quickly when exposed to air.
The picture below shows the explosive reaction produced when potassium is placed in water:
.png)
Metals near the bottom of the series are unreactive. Platinum, for example, will not corrode in air or react with acids. This makes it an ideal metal to make jewellery from as it will not tarnish or be damaged by chemicals.
The picture below shows jewellery made from platinum.

The reactivity series may seem complicated, but there is an easy way to remember it, using this simple mnemonic (or you can make up your own!).
Police Sergeant Charlie MACZITL Has Caught Me Stealing Gold Plates

The reactivity series is often referred to when carrying out displacement reactions. Displacement is when a more reactive metal takes the place of a lesser reactive metal in a compound.
For example, if we have magnesium oxide and we react it with sodium we will get sodium oxide, and magnesium will be left behind. This is because the sodium metal is more reactive than the magnesium metal so it displaces it, meaning it takes its place.
We can represent this in a word equation:
magnesium oxide + sodium --> sodium oxide + magnesium
Let's have a go at the questions now.








