Pythagoras' Theorem states that:
In any right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
In the right-angled triangle below a2 + b2 = c2
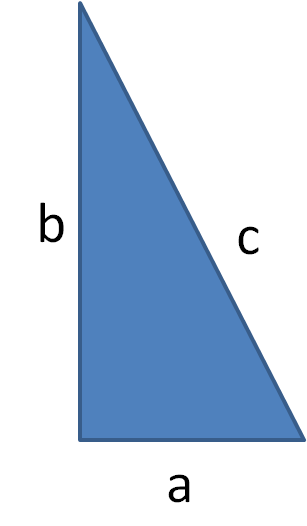
Remember that the triangle must be right-angled and that the hypotenuse is always the longest side and the one opposite the right angle.
Example
Use Pythagoras' Theorem to calculate the length of the side, a, in the following right-angled triangle. Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
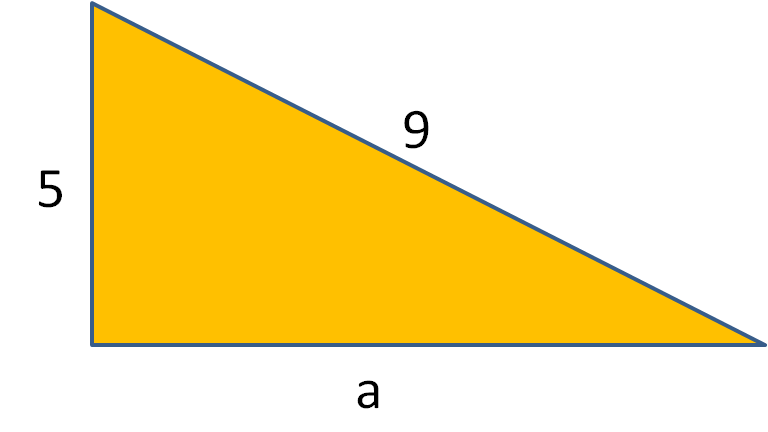
Answer
By Pythagoras' Theorem:
a2 + 52 = 92
a2 + 25 = 81
a2 = 81 - 25 =56
a = √56
c = 7.48 (to 3 s.f.)
Let's have a go at some questions.








