There are a huge range of different types of magnets that we use in society, from small fridge magnets to large magnets used in generators that help us get electricity to our homes.

We also make use of electromagnets, used in televisions, speakers, and in medical technology like MRI scanners.
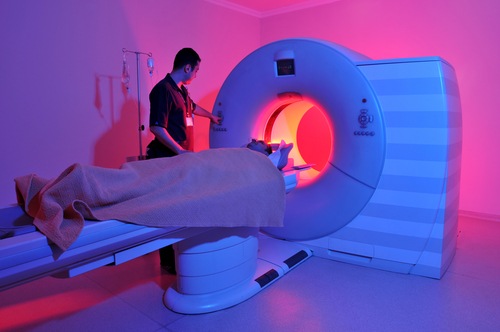
Let's make sure we understand magnets and electromagnets, and the key differences between them!
Permanent magnets have many different shapes, such as bars, horseshoes or buttons.
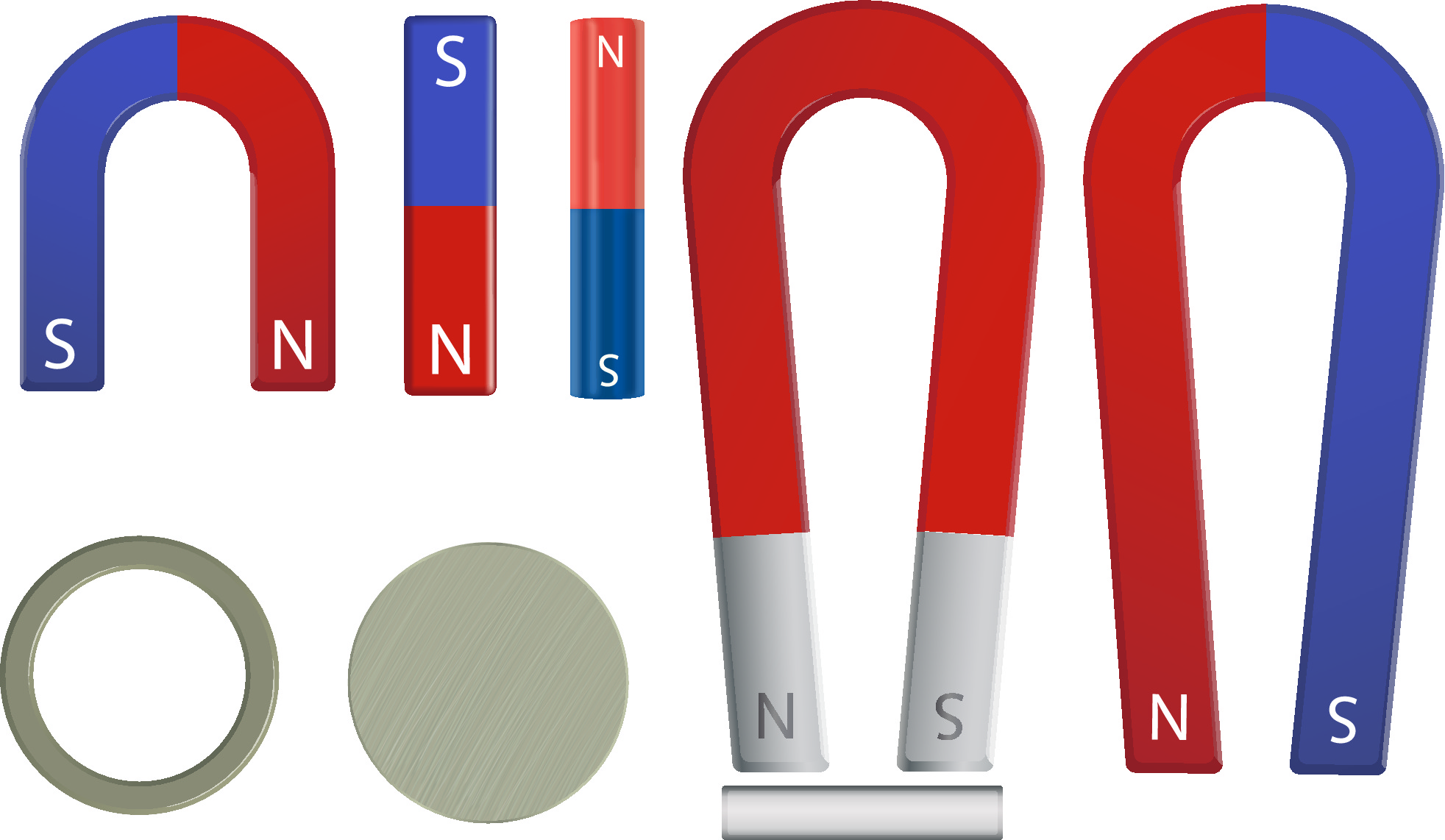
These magnets have magnetic fields around them.
These magnetic fields are areas where other magnets, or magnetic materials like iron and nickel, experience a force.
The magnetic field of a bar magnet looks like this:
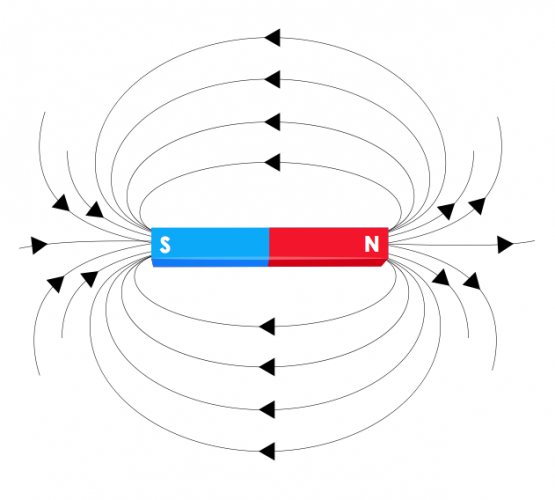
The magnetic field lines show the shape and direction of the field. The field direction is from the north pole to the south pole.
The field is strongest at the poles.
Electromagnets are different to permanent magnets.
Electromagnets can be created by making a coil of wire and connecting it to a power supply or battery.
Typically, the wire is coiled around a soft iron core (a piece of iron that can easily be magnetised and demagnetised).
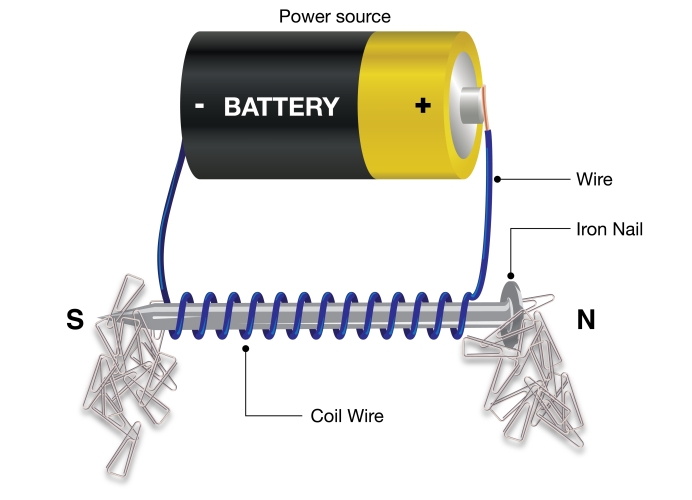
When connected, the electromagnet produces its own magnetic field.
The strength of the magnetic field can be increased by increasing the current in the wire, or by adding more turns to the wire.
Without the iron core, the wire still has a magnetic field. We call an electromagnet without a core a solenoid.
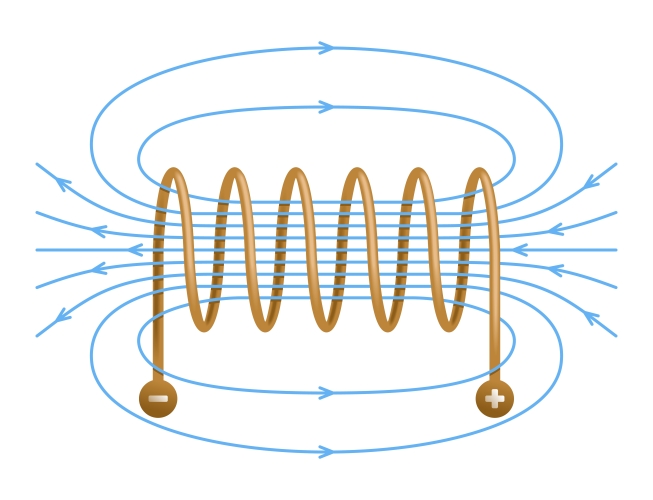
Now let's compare permanent magnets and electromagnets!
Magnetic Field
The magnetic fields of electromagnets and permanent magnets are very similar.
The field lines are closely packed at the poles, indicating the strongest part of the field.
The direction is the same - north pole to south pole.

The main difference is that there are magnetic field lines inside the electromagnet/solenoid and none inside a permanent magnet.
The field lines inside a solenoid are straight and close together. This means that the field is uniform (constant) and strong.
Magnet function
Both magnets and electromagnets attract magnetic materials (iron, steel, cobalt, nickel).
Magnets and electromagnets behave in the same way in terms of attracting and repelling other magnets. Like poles repel, and opposite poles attract.

The biggest difference in function for these magnets is that electromagnets can be turned off and on by switching off and on the power supply. This is not possible with permanent magnets.
These can only stop acting as magnets if they are heated to very high temperatures, or hit/broken up with significant force.
Magnet uses
There are a few factors that affect whether a permanent magnet or an electromagnet is the right choice for a certain role:
1. Strength of the magnet. Electromagnets are often stronger than permanent magnets.
2. Ability to switch on and off. For certain jobs, like magnets for notice boards or fridges, having them permanent is useful. For others, like in the tracks used to propel Maglev trains forward, being able to turn the magnets on and off is essential.

Now let's try some questions!








