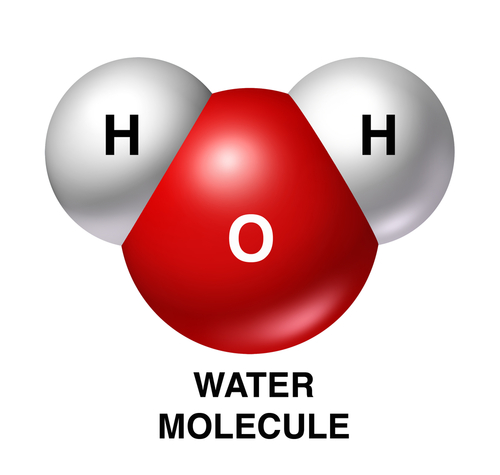
Oxides are chemicals that contain oxygen joined to atoms of other elements. The most common oxide is water - it is chemically called hydrogen oxide, as one oxygen atom is joined with two hydrogen atoms, H2O. The image shows a model of a water molecule.
Carbon forms two different oxides. Carbon dioxide contains two oxygen atoms (di- means two), whereas carbon monoxide (mono- means one) contains one oxygen atom. Carbon dioxide is a gas in the atmosphere used by plants for photosynthesis. It is also produced by animals and plants during respiration. Carbon monoxide is a deadly gas.
Oxides are formed by many elements, metals and non-metals. Aluminium is a metal that does not corrode because it naturally forms a coating of aluminium oxide, as it reacts with oxygen in the air around it. Oxygen in the air reacts with iron causing the rusting of iron. Water is needed for rusting, too.
Metal oxides are solid at room temperature. They are also bases - this means that they form alkaline solutions when they dissolve in water. Non-metal oxides are usually gases at room temperature. When they dissolve in water they form acidic solutions.
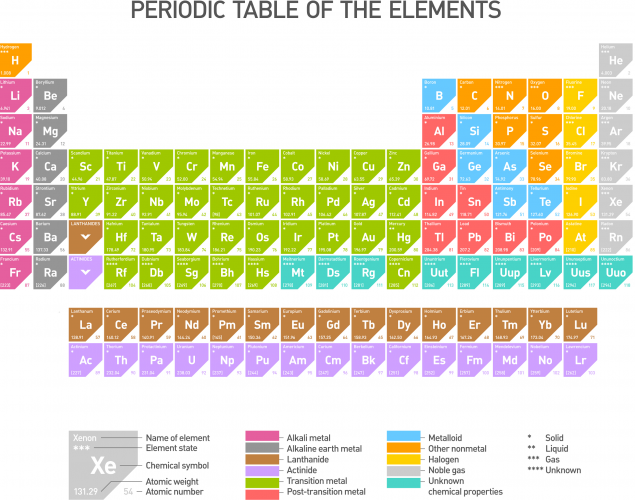
This pattern of behaviour can be explained if we look at the Periodic Table (click on the image to see a larger version).
The metals on the Periodic Table are generally on the left and as we move to the right we start coming across non-metals. As we move from left to right along each period (row) on the Periodic Table, the oxides of the elements become progressively more acidic.
Non-metal oxides, such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide, dissolve in water in clouds and form acid rain.
Right, let's get started on some questions.
If you want to check this page out again, simply click the red help button on the right of the question screen at any point.