Microorganisms (microbes) are tiny living things that can only be seen under a microscope.
People are interested in microbes because they can cause disease in humans, animals and plants.
However, microorganisms can also be very useful. Some can be used to make food and even medicines!
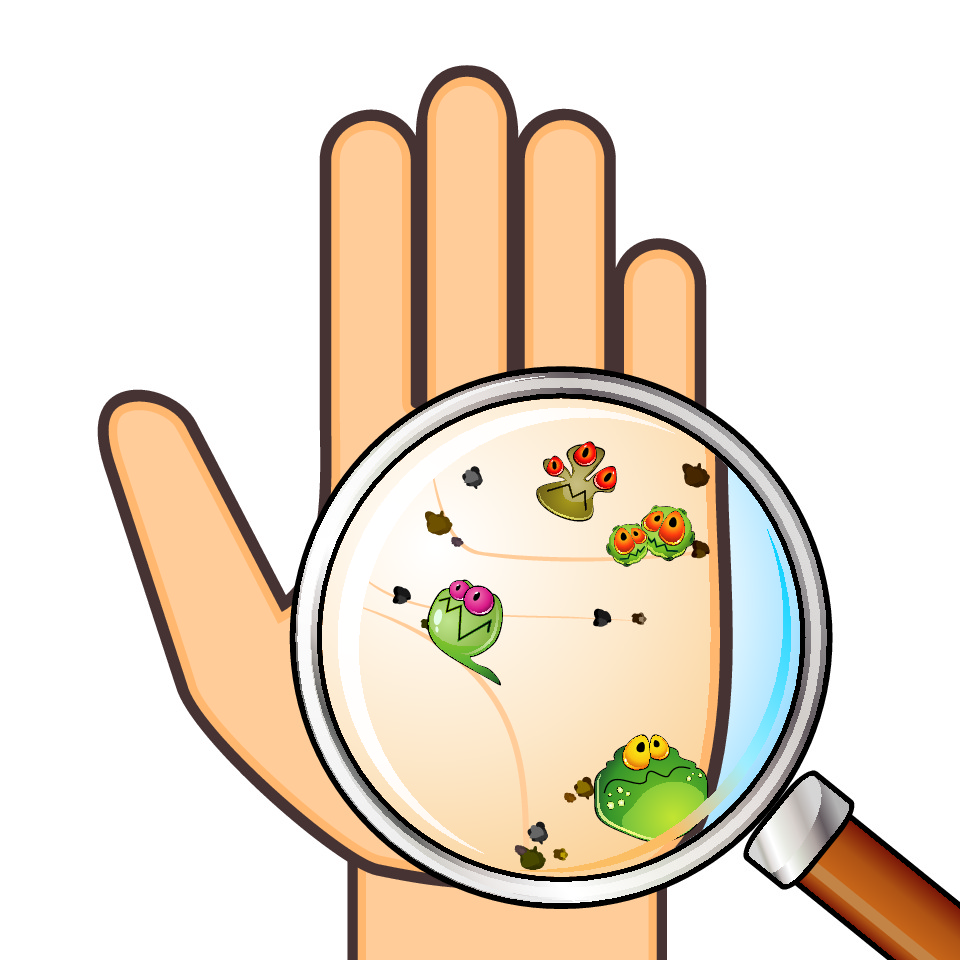
There are at least four types of microorganisms - bacteria, viruses, fungi and protists. The first three are the most commonly known.
Viruses are the smallest, followed by bacteria.
Fungi can also be microscopic, but can also be quite big (think of mushrooms - they are the most well-known type of fungus!).
Protists can also be very small (some are made of just one cell!), although some can be multicellular and be quite big, such as seaweed for example.
Microorganisms require certain conditions to survive and respire. Bacteria, fungi and protists need oxygen and water for respiration. This is why they thrive in moist environments.
Bacteria, in particular, thrive in a warm environment. This is because enzymes work best in warmer temperatures, allowing the cells to grow faster. This is the reason why we put our food in the fridge - it slows down the growth of bacteria. If we leave certain foods out, like milk or cheese, we find they go bad quickly.
Viruses are a little different to other microorganisms. They, interestingly, are not considered to be living. This is because in order to survive they rely on a host cell. The virus takes over the host cell and uses it to make copies of itself - pretty clever!
We rely on microorganisms to make certain types of food, for example, cheese, yogurt and bread.
Different types of bacteria can be added to milk to make specific cheeses. For example, Lactobacillus casei is used to make cheddar cheese, whereas if a fungus like yeast, is added to milk, then stilton cheese is made (shown in the image below).

Bacteria can also be used to make yogurt. Like cheese, specific bacteria can be added to milk to make different types of yogurt.

Yeast, which is a fungus, can be added to dough to make bread. The yeast uses the sugar, or glucose from the dough, to respire. During respiration, the gas carbon dioxide is produced within the bread mixture. This is what makes the bread rise.

Microorganisms are also used in medicines. Alexander Fleming was a scientist who was researching bacteria. He noticed a fungal mould called penicillium had killed certain bacteria. He used this mould to eventually make the medicine we know today as penicillin, a common antibiotic.
In this activity, we will cover the main types of microorganisms, the conditions they need in order to survive and reproduce and how they can be useful to us.