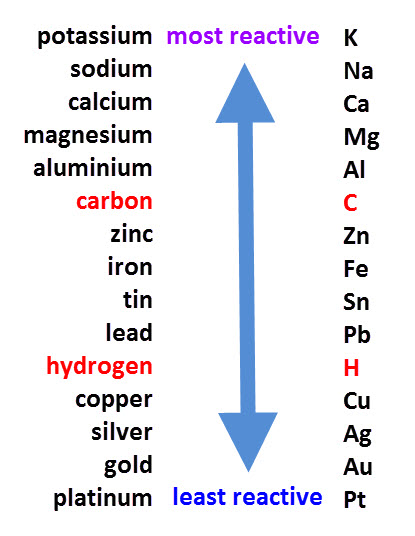
The more reactive metals react with acids to form salt and hydrogen gas. This can be shown in an equation:
metal + acid ![]() salt + hydrogen
salt + hydrogen
Unreactive metals, such as gold, copper, silver etc. do not react with acids.
The three main acids that are used in the science lab are hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and nitric acid (HNO3).
The salt produced depends on the acid that is used to produce it. The table below shows the type of salts that are produced from these acids:
| Acid Name | Type of Salt |
| Hydrochloric acid | Chloride |
| Sulfuric acid | Sulfate |
| Nitric acid | Nitrate |
Hydrochloric Acid
Metals react with hydrochloric acid to produce chloride salts. For example, magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce the salt magnesium chloride:
magnesium + hydrochloric acid ![]() magnesium chloride + hydrogen
magnesium chloride + hydrogen
Mg + HCl![]() 2MgCl2 + H2
2MgCl2 + H2
During this reaction, bubbles of hydrogen gas will be released and the test tube will become hot because it's an exothermic reaction (heat is released).
Sulfuric Acid
Metals react with sulfuric acid to produce sulfate salts:
zinc + sulfuric acid ![]() zinc sulfate + hydrogen
zinc sulfate + hydrogen
Zn + H2SO4![]() ZnSO4+ H2
ZnSO4+ H2
Nitric Acid
Metals react with nitric acid to produce nitrate salts:
magnesium + nitric acid ![]() magnesium nitrate + hydrogen
magnesium nitrate + hydrogen
Mg + 2HNO3![]() Mg(NO3)2 + H2
Mg(NO3)2 + H2
As you can see from the equations, the reaction of a metal and acid produces hydrogen gas. This gas can easily be identified in the lab because it burns with a pop when introduced to a naked flame.
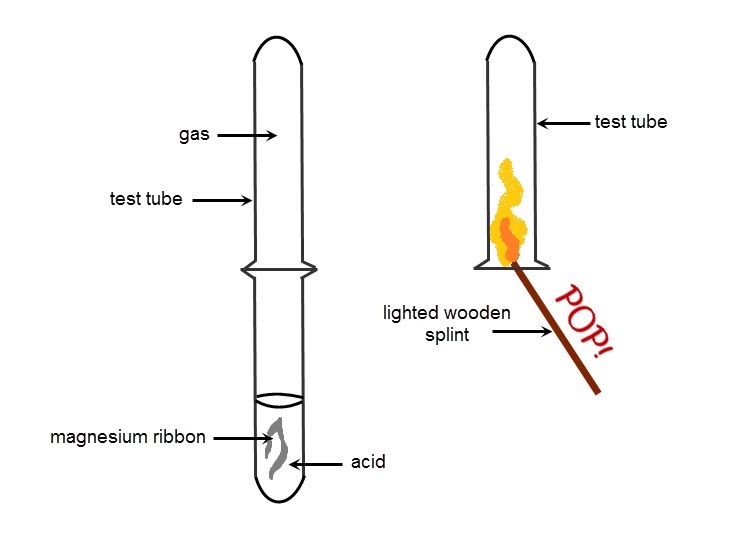
The 'POP!' is the reaction between the hydrogen and the oxygen in the air that produces water vapour.
Let's put that all into context by having a look at a few questions.







