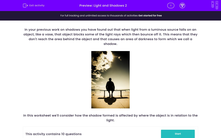
In your previous work on shadows, you have probably found out that when light from a luminous source falls on an object, it blocks some of the light rays. This means that they don't reach the area behind the object and that causes an area of darkness to form, which we call a shadow.

In this activity, we'll consider how shadows are affected by the object's position, in relation to the light.
Objects far away from the source of light

Let's use an example of a source of light that is 93 million miles away from us - the Sun.
When the Sun casts a shadow of a person, a building, a tree, or any object, it will be a sharp, clear shadow.
This is because its rays of light are all travelling in the same direction as each other. The result is a shadow that looks exactly like the object.
Objects close to the source of light
Now think about a different situation - holding your hand directly in front of a light bulb.

If you do this, you will cast a larger shadow that is blurry because the rays of light coming from the source are all travelling in different directions. Therefore, the shadow that is created will not perfectly line up with the shape of your hand.
Have a go at the questions in this activity and see if you can apply these ideas to different situations.