Where does light come from?

An object that produces its own light is called a source of light. Such an object is said to be luminous. The Sun, a light bulb, and fire are three examples of luminous objects.
What happens when light hits things?
Depending on the material, light can be transmitted (meaning it goes through something), reflected (bounces off something), or absorbed (taken in by something).
Transparent materials allow light to pass through, while opaque objects absorb light.
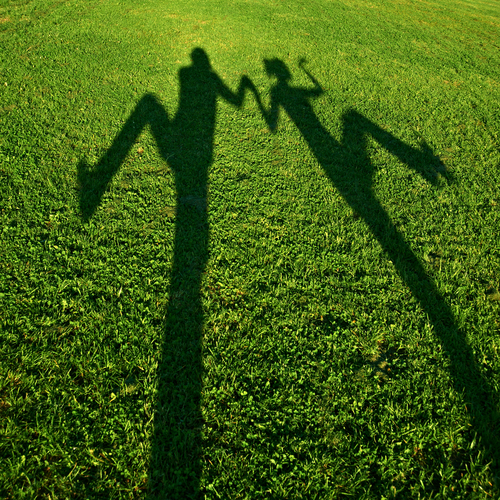
This is how shadows are formed. Think of a sunny day, for example. The Sun in the sky is transmitting its light to the ground, but your body is opaque, and therefore the light cannot reach the part of the ground that you are standing in front of.
The result is a dark region of the ground in the shape of you because you have absorbed that light and blocked the light's path reaching behind you.

How do we see things?
Light travels in straight lines. We see things because light reflects off objects and into our eyes. Our eyes collect this light and our brains then turn it into an image.
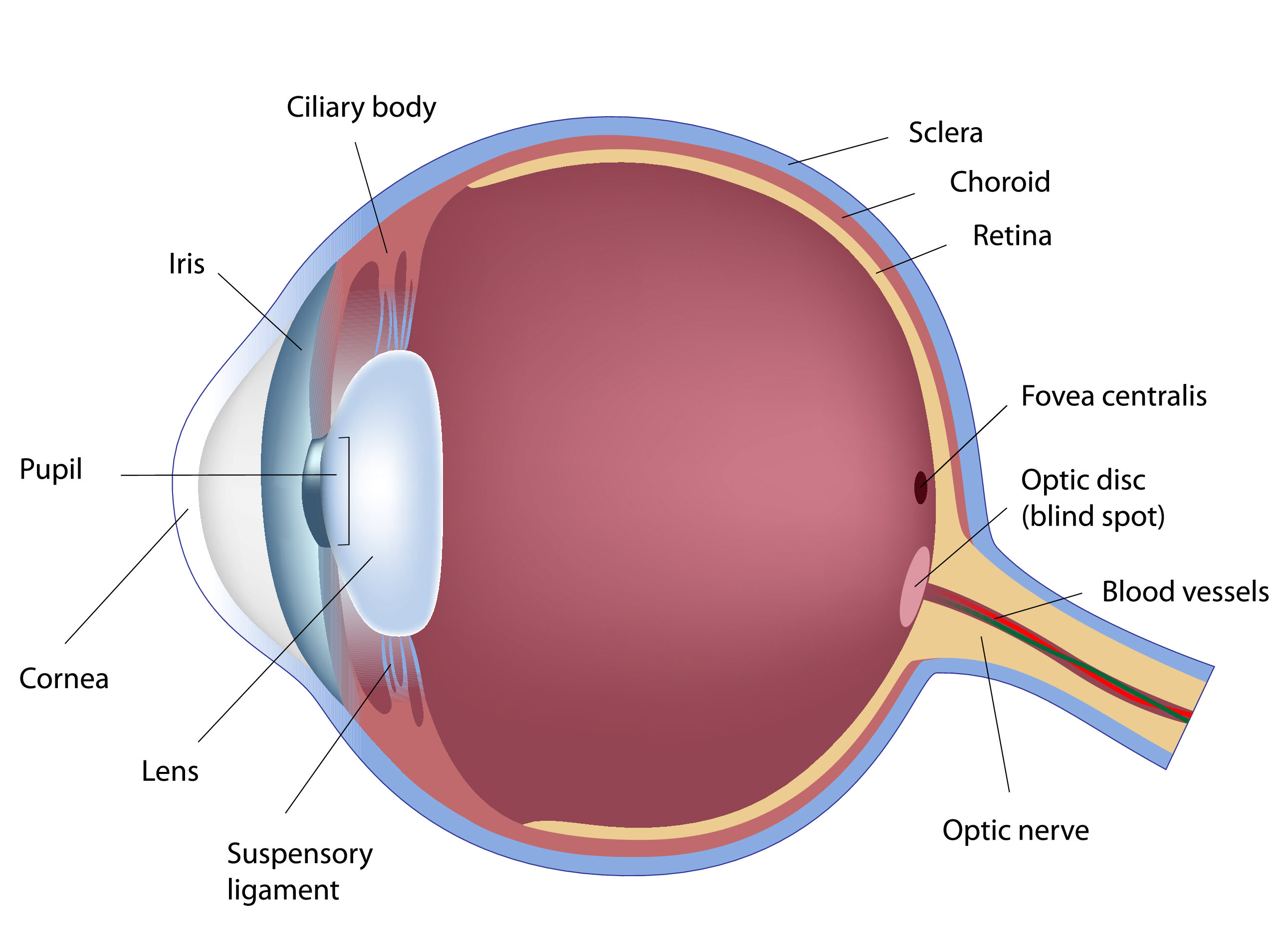
As you can see, the eye is a very complex organ. In simple terms, the pupil is the part of your eye that collects the light. The light is focused by the lens, and it then reaches part of the back of the eye called the retina, where an (upside-down) image forms. The optic nerve is the part of the eye that sends the image to the brain, which automatically flips it the right way up and makes sense of what you are looking at.
Have a good look at this diagram and then let's try some questions all about how we see!