Chromatography is a technique that is used to separate a mixture of soluble substances. That means substances that are dissolved in a solvent.
Some substances are more soluble than others. Substances with a higher solubility move further up the paper.
Chromatography can be used to separate the multiple different dyes in a drop of ink, some food colouring, dyes or plant pigments.
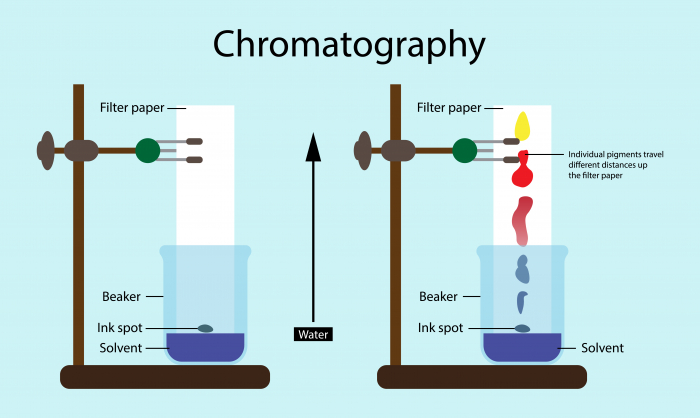
The sample liquids to be tested are dropped onto special paper along a pencil line to ensure the starting place is the same for each sample. The bottom of the paper is dipped in a suitable solvent (this can be water or another liquid). The different-sized particles that make up the samples travel through the paper at different speeds, so they separate at different distances.
The picture below shows the chromatography results for four different inks. It's called a chromatogram. The colours they separated into can be seen by looking at the coloured dots that appear directly above the names of the different inks.
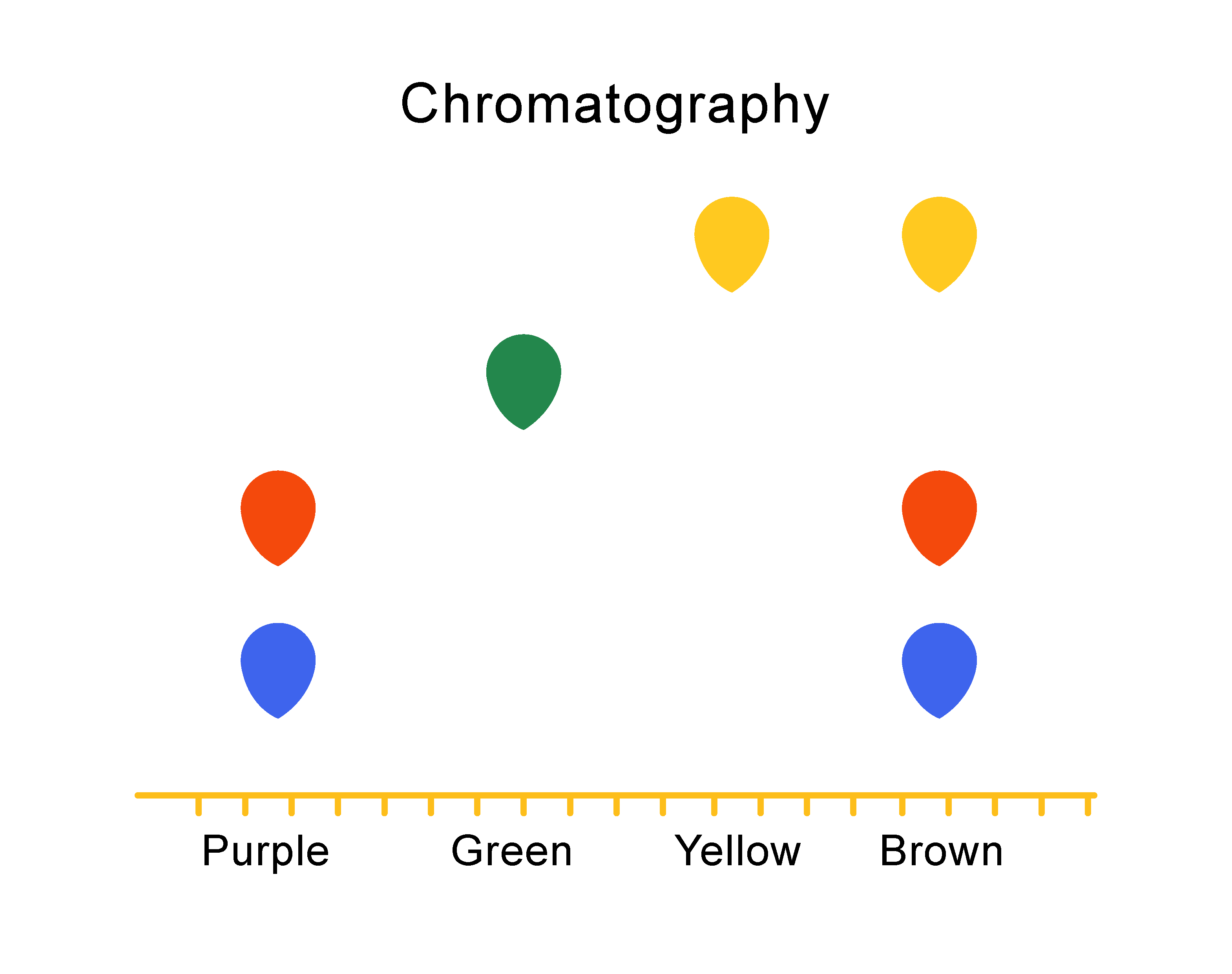
A mixture will separate into more than one spot, in a vertical column. The higher the spot, the more soluble the substance. By matching the colour and height of the spots, you can identify the pigments which were present in the mixture.
So you can see that the brown ink is actually made up of three colours - blue, yellow and red!
On a chromatogram, one spot means that the substance is pure. An impure substance produces two or more spots.
Let's get started on interpreting some chromatograms!







