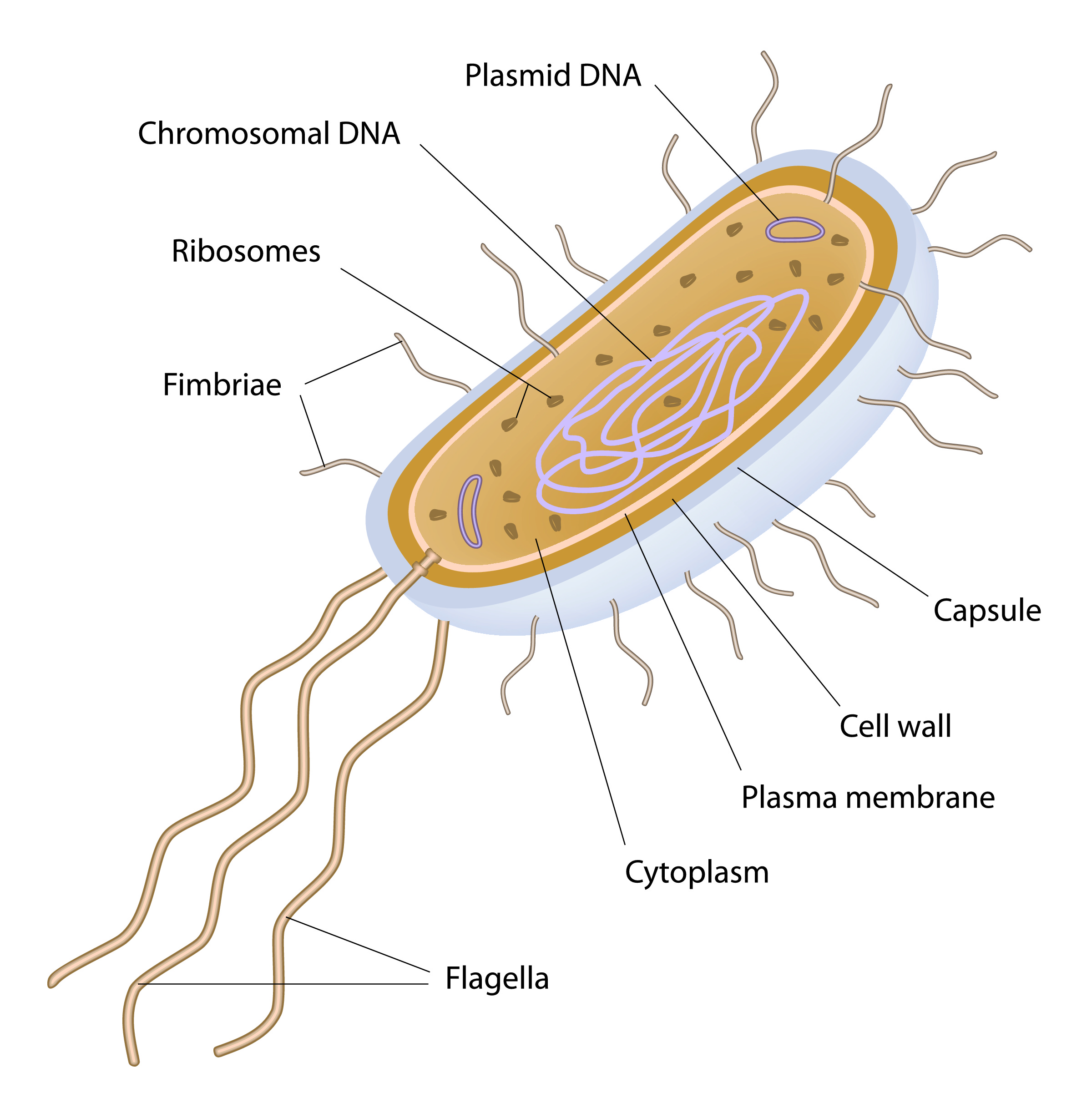
Living things or organisms are made up of cells. Some organisms may be made up of just a single cell (unicellular), like bacteria, whereas others are made up of lots of cells, like a plant. With the invention of the electron microscope in the 20th century, scientists were able to see structures inside of cells more clearly. These structures are called organelles. It was noticed that organisms in the animal and plant kingdom all had a cell membrane, cytoplasm and a visible nucleus that contained the genetic material. These are called eukaryotic cells. Organisms like bacteria are much smaller than eukaryotic cells. The genetic material in a bacteria isn't in a nucleus - these are said to be prokaryotic cells. The genetic material is usually a single loop of DNA, and there may be one or more rings of DNA called a plasmid. Prokaryotic cells have cytoplasm and a cell membrane surrounded by a cell wall.
The organelles in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells differ and have various jobs. Let's look at these organelles a little more closely below:
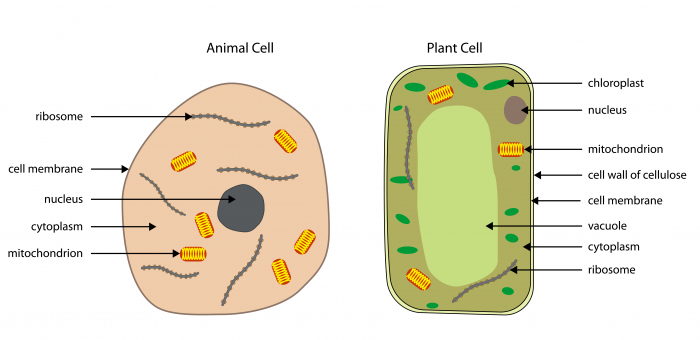
Nucleus- Contains the genetic material which the cell uses to make proteins. Cell activities are controlled here. Kind of like the control centre of a cell.
Cytoplasm - Jelly-like substance that contains the organelles. Many chemical reactions happen here.
Cell membrane - Controls the substances which enter and leave the cell. A bit like the gates at the Houses of Parliament!
Mitochondria - Very small structures in the cytoplasm where respiration takes place, releasing energy for the cell.
Ribosomes - Makes all the proteins needed for the cell.
Some organelles are only found in plant cells, such as chloroplasts, cell wall and vacuoles. Let's look at their jobs below:
Chloroplasts - absorbs sunlight for photosynthesis, the process plants use to make sugar.
Vacuole - sometimes called the permanent vacuole. It's a space in the middle of the cell filled with cell sap - it keeps the plant rigid to support the plant.
Cell wall - made of fibres to make the cell stronger and supports the plant.
Prokaryotic cells have some similar features to eukaryotic cells, like the cytoplasm, cell membrane and cell walls.
However, the cell wall in prokaryotes is made of a different substance than in plants, and its role is to maintain the cell's shape and protect the cell. The cytoplasm and cell membrane do similar roles as in eukaryotic cells.
In the following activity, you will identify and describe the key features of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Want a bit more help with this before you begin? Why not watch this short video?








