A catalyst is a substance you may come across in biology or chemistry. And even at home when you do the washing!
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction.
Often, the chemical reaction will take place on its own anyway, but maybe very slowly. By introducing a catalyst into the reaction, you can make the reaction take place faster.

Catalysts make the reactants turn into products faster.
How does it do this? Well, in order for a chemical reaction to take place, the particles involved need enough energy to enable them to collide and react. A catalyst lowers the amount of energy that the particles need in order to react. This means that less energy is needed for a reaction to take place. More particles are therefore likely to have enough energy for successful collisions to occur. So there are more successful collisions and a faster reaction as a result!
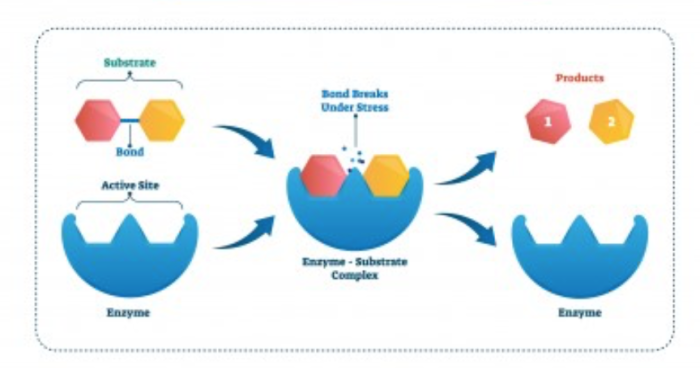
A catalyst is not used up once it takes place in a chemical reaction. This means that they come out of the reaction the same as they went in, so they can be reused. We can see this below.
Catalysts are often put into washing powder to enhance the breakdown of stains on our clothes - washing powders with catalysts in them are called 'biological washing powders'. This is because they contain biological catalysts called enzymes that break down things like carbohydrates, proteins and fats from our foods.

How does it do this? The enzyme has a certain shape, and allows the substrate to fit into it, where it speeds up its breakdown, before releasing the products. Notice that the enzyme is not changed at all during the process, and it is free to go and act on another substrate.
Let's try some questions on this topic of how catalysts work.








