There are five shapes that you will need to be able to find the area of.
These are rectangles, triangles, parallelograms, trapeziums and circles.
We will not be using circles in this activity, but let's quickly remind ourselves of the formulae for the other four shapes we will be using.
Review
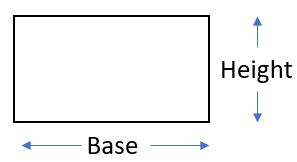
Rectangles:
The area of a rectangle is given by Area = Base x Height (A = bh).
Triangles:
The area of a triangle is given by Area = 1/2 x Base x Perpendicular Height (A = bh/2)
Be careful of two things here:
You must use the perpendicular height (the one at 90o to the base).
You must remember to divide by 2!
Parallelograms:
The area of a parallelogram is given by Area = Base x Perpendicular Height (A = bh).
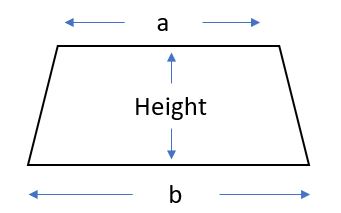
Trapeziums
The area of a trapezium is given by Area = 1/2 x Sum of the Parallel Sides x Perpendicular Height (1/2 x (a + b) x h)
Be careful of two things:
You must remember to divide by 2.
a and b are the parallel sides, remember that they might be the top and bottom sides, or the right and left sides.
Example
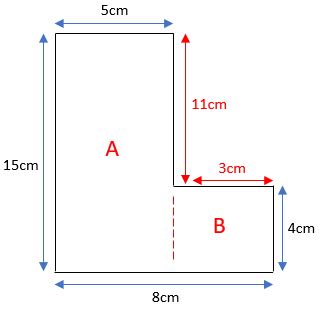
Find the area of this compound shape:
Split the shape into two or more shapes that we can deal with. In this case, it splits nicely into two rectangles.
Work out the lengths we are not given. We may not need them, but it's useful to have them in case we do.
Label the shapes separately so you know which one you are talking about in your working.
The base of A is 5 cm and the height of A is 15 cm. The area of A is 75 cm2
The base of B is 3 cm and the height of B is 4 cm. The area of B is 12 cm2
The total area of the shape is 75 cm2 + 12 cm2 = 87 cm2
Are you ready to find some areas?