

Great, this is what we have been waiting for. Time to top up the tan!
Okay so maybe not that sort of "tan".
We can use the tan ratio to help us find a missing side length in a right angled triangle.
We are going to look at Tan here and what the "TOA" means.
A formula triangle is helpful:

T is for Tan (which will be given as an angle)
A is for adjacent side
O is the opposite side
The line in the middle means divide.
To use this triangle we cover up what side it is we want to find and we are left with a formula to follow.
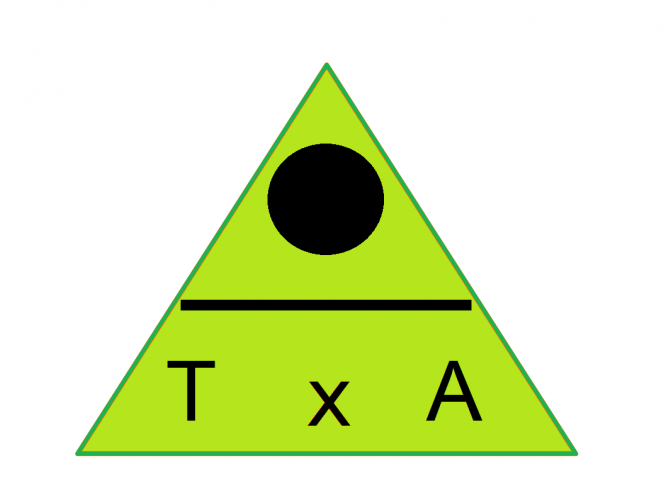
If we want to find the opposite side, cover up the O. The formula we are left with is Tan(angle) x Adjacent.
O = T x A
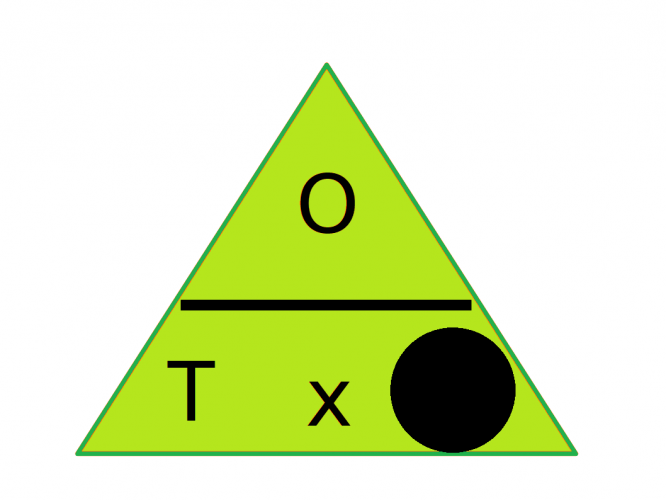
If we want to find the adjacent, cover up the A. The formula we are left with is opposite divided by Tan(angle)
A = O ÷ T
Let's look at some examples.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Make sure your calculator is set to degrees otherwise this formula will not work correctly. (You should see a D at the top of the calculator screen if it is in the correct mode).
Example 1
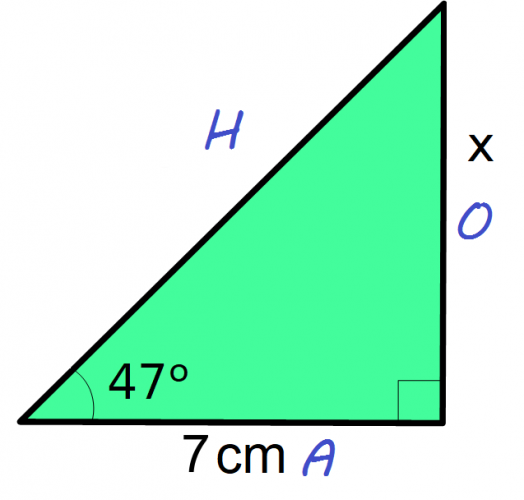
1. Label the lengths of the triangle: A, O, and H
2. Work out the side you want to find. In this case, x is the opposite length, so we want O
3. The formula triangle shows that O = A x T
4. Substitute the angle and the length into the formula. This gives O = 7 x tan47
5. In your calculator type in 7 x tan 47
6. Your answer should be 7.51 cm to 2 decimal places.
Example 2
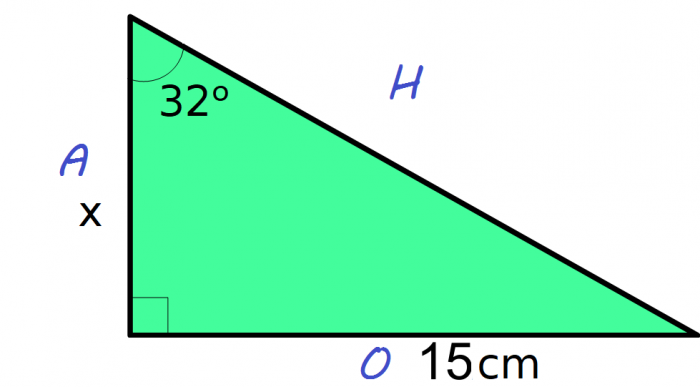
1. Label the lengths of the triangle: A, O, and H
2. Work out the side you want to find. In this case, x is the adjacent length, so we want A
3. The formula triangle shows that A = O ÷ T
4. Substitute the angle and the length into the formula. This gives A = 15 ÷ tan 32
5. In your calculator type in 15 ÷ tan 32
6. Your answer should be 24.00 cm to 2 decimal places.








