Did you know there are between 30 to 40 trillion cells in the human body?! It's hard to be precise though as cells are continually being replaced.
We know that cells that are the same type form a group called tissues, and tissues form groups called organs. These organs carry out a range of different functions to ensure that the organism operates correctly.
Each organ, whether it is animal or plant, is made up of tissues which are groups of the same sort of cell. For example, a leaf is made up of many different tissues: the epidermis, the palisade mesophyll, the spongy mesophyll and the cuticle, to name just a few! An animal's skin also contains different tissues such as the dermal tissue, epithelial tissue and the subcutaneous tissue.
Here are some of the most common organs from the human body:
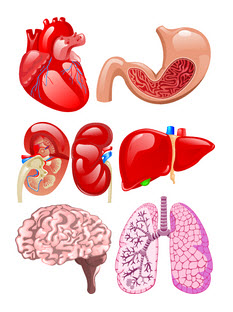
Some of the most vital organs for humans, and indeed most animals, are the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, stomach, intestines and brain. Each of these organs has a specific function to perform to keep the body alive. For example, the function of the heart is to pump blood around the body, the brain co-ordinates all the functions of the body, the stomach, liver and intestines all work together to digest food, and the function of the lungs is to enable us to breathe.
Did you know that plants also have organs? Some of the most important organs found in plants are the root, leaf, stem and flower, all of which have important functions to perform. The root and stem are important in transporting water and minerals around the plant, the leaves use sunlight to make glucose and the flowers attract insects to enable pollination to take place.

Different organs work together to form organ systems. For example, in the human body the circulatory system is made up of the heart, arteries and veins. The function of the circulatory system is to transport substances like oxygen and nutrients in the blood around the body.
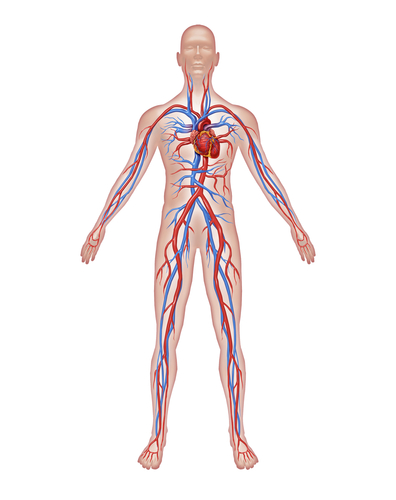
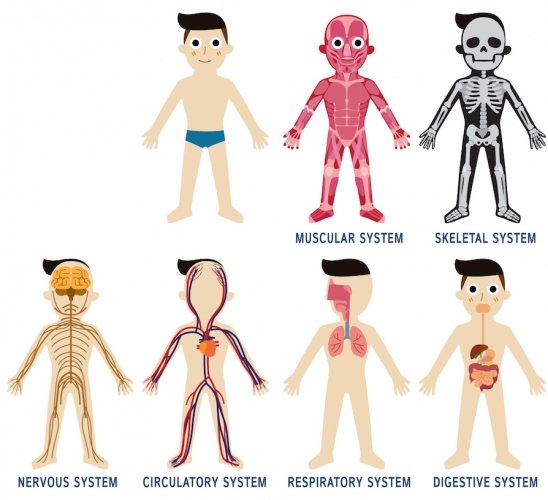
The human body has many organ systems. Here are some examples summarised below:
| Organ System | Organs Involved |
Function |
| Circulatory System |
Heart, arteries, veins |
Transports oxygen and nutrients around the body |
| Digestive System |
Stomach, liver, small and large intestines |
Breaks down food to provide nutrients |
| Reproductive System |
Vagina, uterus, penis, testes |
To produce offspring |
| Nervous System |
Brain, spinal cord |
To control body activities |
| Locomotor System |
Muscles, bones |
To allow movement |
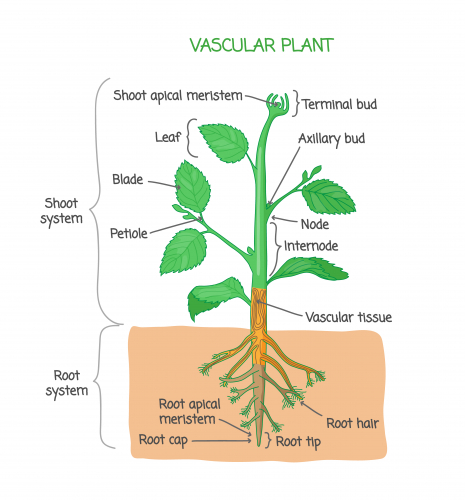
Plants also have organ systems. The leaves, stem, flowers and fruits form part of the shoot system. These are found above the ground, whereas the root system consists of the organs beneath the ground, like the roots and storage organs.
In this activity, we're going to look at how cells, tissues and organs work together to form organ systems.







