What is a fluid?
A fluid is a substance that can flow. Therefore, liquids and gases are both fluids. They are able to flow because their particles are not in a fixed position and are able to slide over each other.
.jpg)
A cloud forms when water vapour turns from gas to a liquid. In each state, it is a fluid.
Shape
One of the properties that defines liquids and gases is that they do not have a fixed shape. This means that they can be poured into a container of any shape, and they will take the shape of that container.



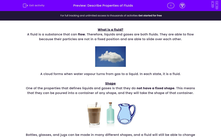
Bottles, glasses, and jugs can be made in many different shapes, and a fluid will still be able to change shape to fill it with no gaps.
Volume
Volume tells us how much space something takes up. It is measured in metres cubed, or litres for fluids. This is where liquids and gases have a difference in their properties.

Liquids have a fixed volume. This means that a liquid will remain the same 'size', regardless of where it is or the conditions it is under. For example, if you poured 2 litres of water from a jug into a cup, you would still have 2 litres of water.

On the other hand, if you had a bottle holding 5 litres of gas and opened the lid, the gas would escape and it would spread out. Therefore, it would no longer occupy 5 litres. Gases do not have a fixed volume. They can either expand ('grow') or contract ('shrink') due to changes in pressure and temperature.
Compressibility
The final property we will look at is compressibility, and this just means whether or not the substance can be squashed.
Compressing a substance means forcing it into a smaller space. As we have just seen, liquids have a constant volume, so it is not possible to compress liquids. When held in a container, applying a downwards force on the liquid will not force it to shrink.

Meanwhile, gases, due to having much more space between their particles, can be compressed. You can 'squash' a gas in a syringe for example, by pressing the top with your thumb.
Now that you have seen the similarities and differences between liquids and gases, let's have a go at some questions.