Acids and alkalis react together to form new products in a neutralisation reaction.
If exactly the right amount of alkali is added to an acid, the resulting solution will have a pH of 7 because the acid and alkali will 'cancel' each other out.
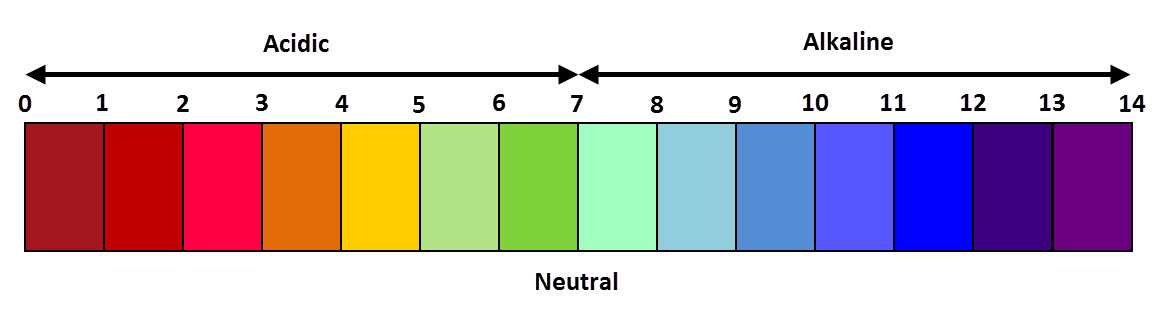
This means that the pH of the acid increases towards 7 during neutralisation, but the pH of the alkali decreases towards 7.
Neutralisation reactions are performed every day. For example in the treatment of acid indigestion, or a farmer adding quicklime (an alkali) to his fields to neutralise acidic soil.
Acids and alkalis can also be used to treat insect stings:

Bicarbonate of soda (an alkali) can be used to treat bee stings which are acidic.

Vinegar (an acid) can be used to treat wasp stings which are alkaline.
Just don’t get the two mixed up or it may make the sting more painful – ouch!








