We need to know the arrangements of particles in solids, liquids, and gases.
We also need to be able to recall the names for each change of state. A flow diagram summarising each change is shown below.
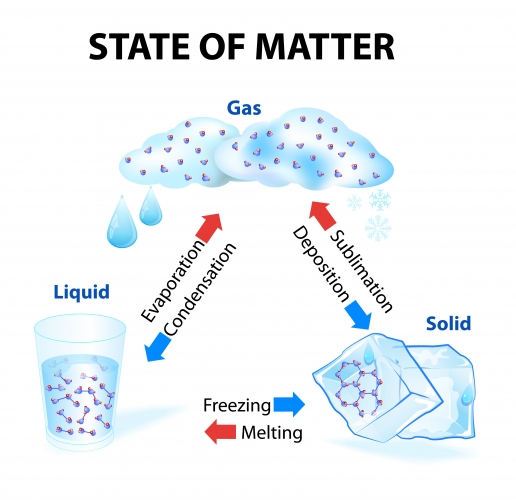
Notice that some of the arrows are red and some are blue.
The red arrows represent changes that involve an increase in temperature (i.e. melting, evaporation, and sublimation need you to heat something up).
The blue arrows represent changes of state that involve a decrease in temperature (i.e. condensation, freezing, and deposition need you to cool the substance down).
You should also be familiar with the terms 'melting point' and 'boiling point'.
The melting point is the temperature at which a particular solid turns into a liquid (and the same temperature that the liquid turns back into a solid).
The boiling point is the temperature at which a substance evaporates and condenses. For example, the boiling point of water is 100ºC, meaning that water turns into vapour (and vapour turns back into water) at this temperature.
That's a lot to take in, so remember that you can look back at this page at any point by clicking on the red help button on the screen.
.jpg)
Let's try some questions!








