Ever wondered why your urine is often darker and more concentrated in the summer? Probably not, it's not the nicest thing to be thinking about!
Often, it's because we tend to sweat more in the summer months, so we lose a lot more water. Our kidneys then try to keep a hold of more water for many of our important processes, resulting in more concentrated urine!
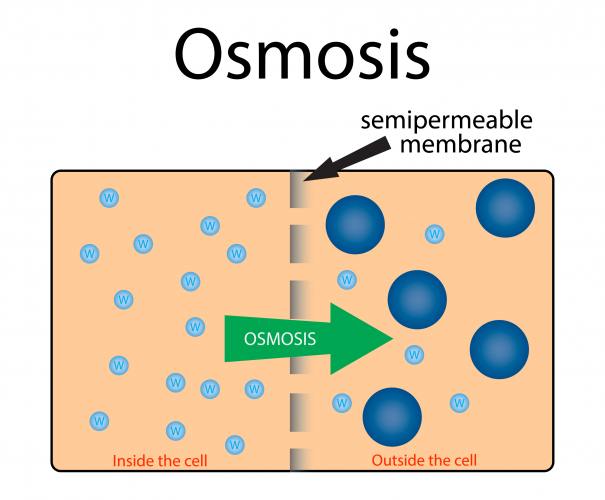
Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules from a low concentration solution to high concentration solution, across a partially permeable membrane.
A partially-permeable membrane has holes or pores in it that allow water molecules through, but are too small to allow larger molecules through.
During osmosis, water molecules diffuse from pure water or dilute solution to more concentrated solutions:
Dilute solutions have a high concentration of water molecules.
Concentrated solutions have a low concentration of water molecules
Osmosis in organisms
Plant and animal cells are surrounded by a partially-permeable plasma membrane. This allows water and other small molecules to diffuse across. Plant cells additionally have a strong cell wall surrounding the membrane, which offers support and protection. Animal cells don't have a cell wall. This means they respond differently to plant cells to the gain and loss of water.
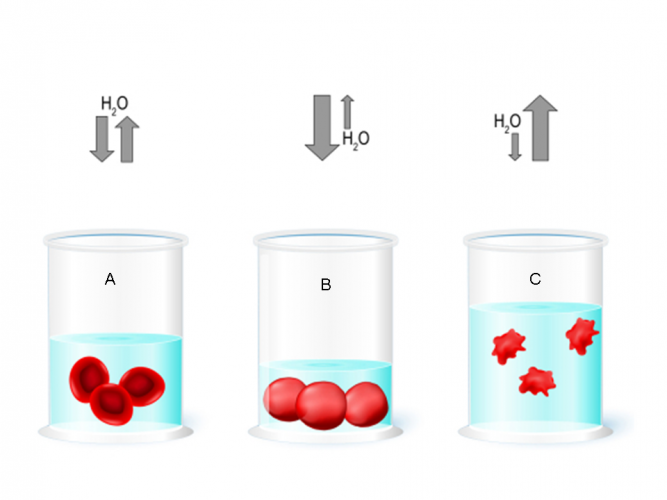
In dilute solutions, osmosis can cause animals' cells, such as red blood cells, to swell up and sometimes even burst (Beaker B in the image above). This is because water will move from a high concentration outside the cell to a lower concentration inside the cell. In concentrated solutions, water loss causes the cells to shrink (Beaker C in the image above). Animal cells need to maintain a balance. This means that the water concentration both inside and outside the cell are equal.

Plants require water in order to photosynthesise. The roots of a plant contain root hair cells which are specialised cells that increase the surface area of the cells for maximum absorption of water by osmosis. In pure water, plant cells will take in water via osmosis and become firm or turgid. In a concentrated solution, where there is not much water present, the cell loses water and starts to shrink and becomes flaccid.
In humans, the concentration of water and salt in the blood are controlled by the kidneys. The kidneys ensure we have the right concentration of water and getting rid of the excess water as urine.
In the following activity, you will define and describe osmosis.








