Throughout the topic of electricity, you will have become familiar with conductors like iron and copper.
But what about the metal mercury?

Mercury is a liquid at room temperature - and it can conduct electricity! Let's learn about the different types of liquids that can conduct electricity.
First, a reminder of the definition of the word conductor. An electrical conductor is a material that allows electrical current to flow through it.
Metals are good conductors of electricity, and some are better than others. For example, copper is a better conductor of electricity than aluminium.
Why do metals conduct electricity?
Metals contain many free electrons - tiny negatively charged particles. Charged particles can carry electrical energy.
In the diagram above, you can see that the electrons can flow through the conductor when provided energy by the cell.
So, what about mercury?

Mercury is a metal, but it is unusual because it is a liquid at room temperature. It still shares many properties with metals though - mercury is dense, and shiny, just like most other metals.
Mercury can also conduct electricity. Mercury has free electrons, and if liquid mercury is used in a circuit connected to a battery, those electrons can move and conduct electricity.
Now let's imagine molten copper. If you heat copper to 1085 ºC it would melt and become a liquid.
In its liquid form, copper would still be a good conductor of electricity.
Molten metals are good conductors of electricity. However, most metals conduct better as solids than liquids because their internal structure allows more free electrons to travel though easily.
What about other liquids?

Let's consider seawater. Seawater has a lot of salt dissolved into it.
You might know that salt is a compound made of sodium and chlorine, so the chemical name for salt is sodium chloride (NaCl)
When salt is dissolved into water, the salt separates into two charged particles called ions. Water with salt dissolved in it contains sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-).
We know that charged particles can transmit electricity, and these ions are examples of charged particles.
Just like free electrons can carry electrical energy in a copper wire, charged ions can carry electrical energy in liquids.
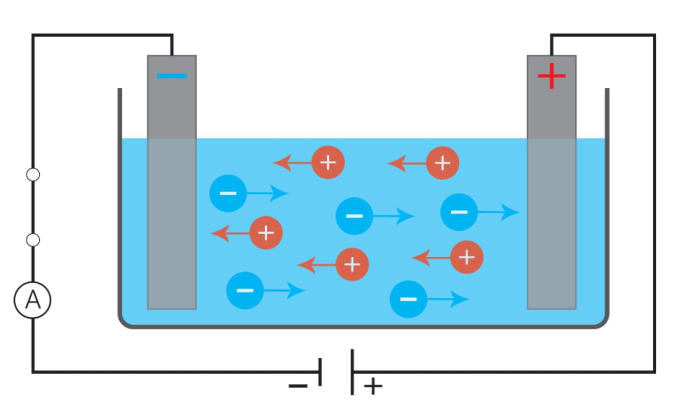
In this image, we can see negatively and positively charged ions dissolved in water. When a cell provides electrical energy to the circuit, the ions can move, carrying that electrical energy with them.
A liquid that can conduct electricity like this is called an electrolyte.
Pure water is not a good conductor of electricity, but water with dissolved ions and minerals is. So, a bit like seawater, rain water, and tap water, can both conduct electricity.
Liquids with dissolved charged ions can conduct electricity.
Some liquids, like vegetable oil or honey, do not have dissolved charged ions. They also don't have free electrons. So, they are insulators - they do not allow electricity to flow through them easily.

That's quite a lot to take in, so remember that you can look back at this page at any point by clicking on the red help button on the question screens.
Let's have a go at some questions!