
Alcohol is so common that we don’t often think about it as a drug, but it is. Alcohol is known as a recreational drug. A drug is simply a chemical that can affect the way your body works. Other recreational drugs include caffeine and nicotine found in cigarettes - these are legal drugs. However, most other recreational drugs are illegal, such as cocaine, ecstasy and heroin.
What type of drugs are there?
There are many different types of drug which will affect your body in different ways. Alcohol, or ethanol (the chemical in alcohol) is classed as a depressant, as it slows down the messages to your brain and nerves. Other depressants include drugs such as cannabis, solvents (such as aerosols and glue) and heroin.
The nicotine found in cigarettes stimulates the nervous system, so is known as a stimulant. Other stimulants are drugs like cocaine, ecstasy and amphetamines.
So, what does alcohol do to the body?
Your body can only process one unit of alcohol an hour. Drinking a lot of alcohol in a short space of time can stop the body from working properly.
High levels of alcohol in your blood can:
- Slow down brain functions such as thinking, decision making and muscular activity
- Affect your sense of balance
- Irritate the stomach, causing vomiting
- Lower the body’s temperature, which can lead to hypothermia
- Cause dehydration, which could lead to permanent brain damage
- Affect the nerves that control your breathing and heartbeat - it can stop both
Splitting headaches, sickness, dizziness, dehydration...a hangover is the unpleasant experience the morning after the night before.
Many people experience a hangover if they have consumed too much alcohol, as it is a diuretic. This means it removes fluids from the body. Drinking excessively can lead to dehydration, and most of the symptoms of a hangover are simply due to your body being dehydrated.
What are the long-term effects of alcohol?
The effects of a hangover are short-lived and usually only last for about a day. However, this does not mean that the alcohol has not affected the parts of your body that you can’t see.
The liver – drinking alcohol damages the liver and can lead to cirrhosis of the liver (permanent loss of liver function). This is because the blood from the stomach directly enters the liver, carrying with it the ethanol that has been drunk.
Brain development – the areas of the brain responsible for behaviour, emotions, reasoning and judgement are still developing throughout childhood and into the teenage years. Drinking during this time can have a long-term impact on memory, reactions and attention span. Alcohol can lead to damage to nerve cells in the brain. Alcohol can also starve cells of oxygen, leading to strokes.
Weight - alcohol can lead to weight gain due to the calorie content of commercial alcoholic drinks.
Fertility – it is recommended that alcohol is avoided if a couple are trying to conceive a baby. Alcohol can interfere with hormones and ovulation, which is the time when a woman's ovaries releases an egg cell. This can be disrupted making it harder for a woman to become pregnant.
Alcohol can also increase the risk of developing cancers such as liver, bowel, breast and mouth cancer. Alcohol damages our cells and our body is unable to repair the damage. Alcohol can lead to our cells dividing more than normal increasing the chance of cancers.

What does smoking do to the body?
Nicotine
Nicotine is the addictive drug that causes smokers to crave cigarettes. It occurs naturally in the tobacco plant to help protect it from insects. When it enters the human body, it stimulates the nervous system, causing an increase in pulse rate and blood pressure.
Carbon monoxide
When tobacco is burned, the gas carbon monoxide (dubbed 'the silent killer' due to its colourless, odourless and toxic nature) is released. It is an extremely dangerous gas. Once in the bloodstream, it prevents the blood from carrying oxygen properly around the body.
Tar
The residue of the smoke from burning tobacco is tar. Tar is a sticky, dark brown substance that can accumulate and coat the airways and lungs. This tar coating then makes gas exchange in the alveoli very difficult.
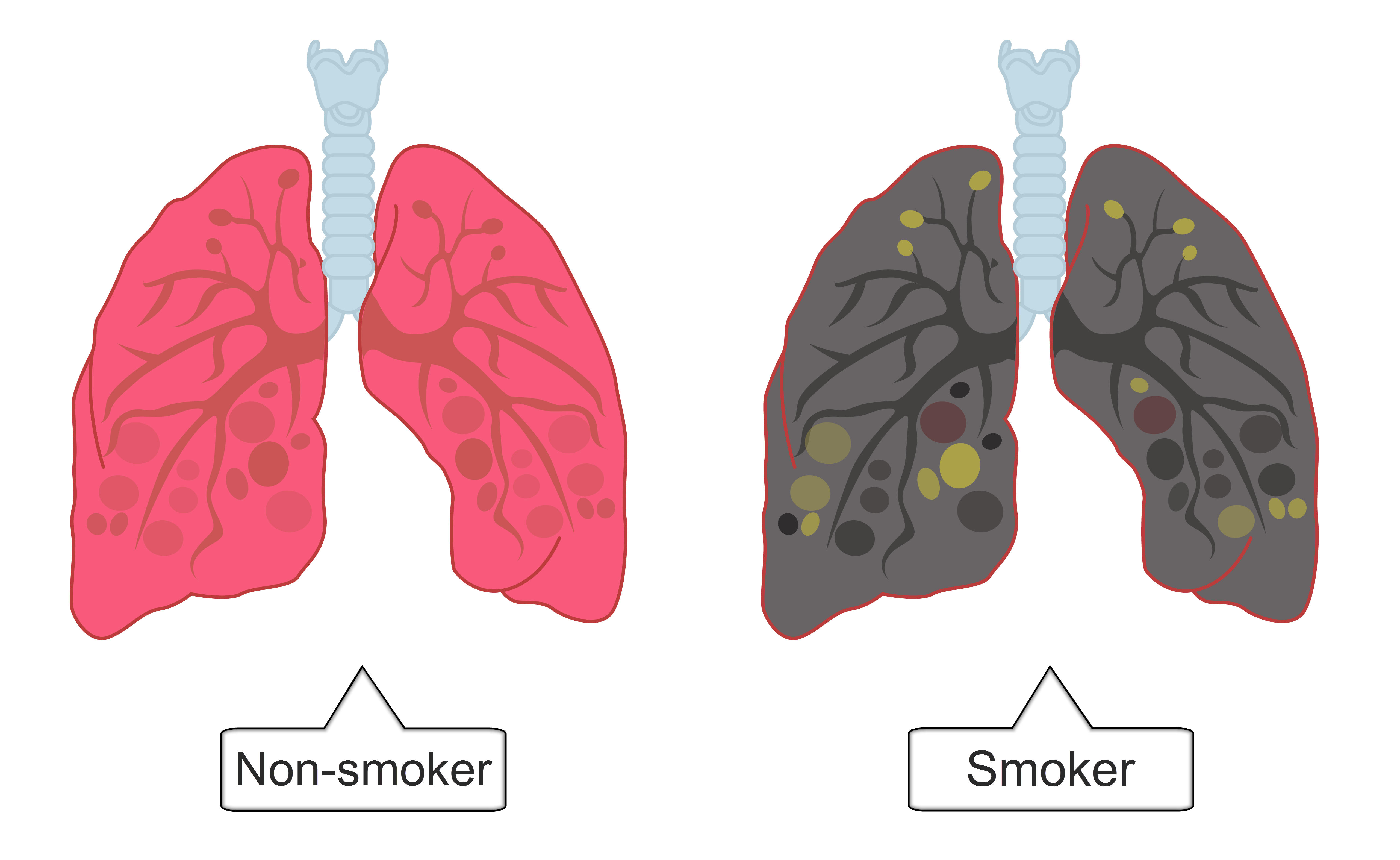
In the lungs, the cells that line the bronchi produce sticky mucus, which traps dirt and microbes. These cells have tiny hair-like cilia, which normally move the mucus and trapped dirt out of the lungs. The smoke and tar from cigarettes, however, damages the cilia, causing smokers to cough more in order to get rid of the mucus. This can ultimately lead to bronchitis.
Tar also contains other harmful substances, including carcinogens which can cause cancer.
Smoking and Cancer
Cancer is an uncontrolled growth of cells resulting in the formation of a tumour.
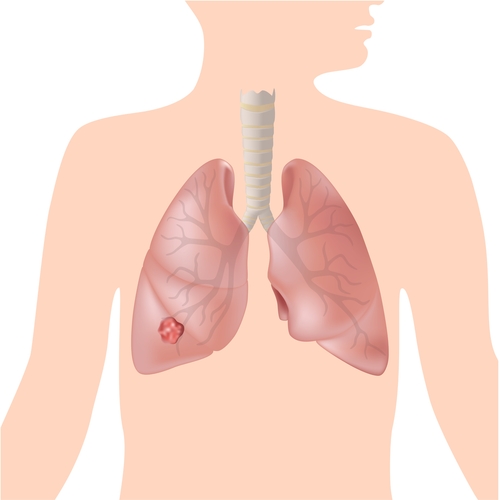
Tobacco and cigarettes are known to cause cancer in the lungs, airways, throat, voice box and mouth. 9 out of 10 people who die from lung cancer are smokers.

How about other drugs? What do they do to the body?
Drugs like cannabis, solvents and heroin can:
- Slow down brain functions such as thinking and muscle movement
- Cause blurred vision or hallucinations
- Slow down pulse rate and lower blood pressure
- Cause impaired judgement and coordination
Drugs like cocaine, ecstasy and amphetamines can:
- Increase heart rate and body temperature
- Give more energy and confidence
- Cause damage to the heart
- Lead to memory loss
- Cause lack of concentration
There are many long term effects of drugs on the body - these vary depending on the type of drug.
Here are just a few:
- All recreational drugs can be addictive - this is when the brain becomes reliant on the chemical found in the drug
- Damage to the liver is common as it is the organ which breaks down drugs in the body
- The injecting of drugs can also lead to various diseases such as HIV and hepatitis, caught through the use of contaminated needles
In this activity, we will compare how alcohol, smoking and drugs affect the human body.
You can look back at this introduction at any point by clicking the red help button on the screen.







