Combustion (or burning, as it is more commonly known) is the reaction between a fuel and oxygen which can create lots of energy.
The oxygen required for this reaction comes from the air. The air is a mixture of gases.
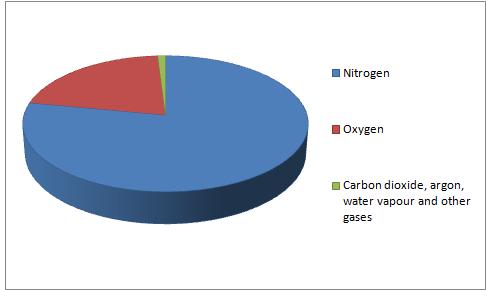
It is mainly composed of:
Nitrogen (about 78%)
Oxygen (21%)
A small mixture of other gases such as carbon dioxide and argon.
This can be shown in a pie chart:
During combustion, oxides are also produced - often in the form of carbon dioxide. This is because fuels are reacting with oxygen.
When the flammable metal magnesium is burned, lots of light, heat and smoke are produced, but when the reaction is complete the white solid magnesium oxide will be clearly seen.
This process is called oxidation and this reaction can be seen in the 'sparklers' that are used on Bonfire Night.

This reaction can be shown in a word equation:
Magnesium + Oxygen ![]() Magnesium oxide
Magnesium oxide
Note that the light, heat and smoke are not included in the chemical (word) equation because they are not chemicals.
All combustion reactions are irreversible. This means we can't reverse the reaction - we won't get the original reactants (what we react) from the products (what we make). So in the example above, we can't get magnesium or oxygen back from the product, magnesium oxide.
Another example of oxidation is:
Potassium + Oxygen ![]() Potassium oxide
Potassium oxide
The energy produced by combustion can be put to many uses - from heating your home and cooking your food, to powering your car. The fuels used to provide energy for these uses are not metals, like magnesium, they are more likely to be petrol, diesel, and natural gas.
Let's have a further look at combustion in the questions that follow.







