Substances can change state when they are heated or cooled.
This diagram shows the processes that take place when substances, in this case water, changes state.
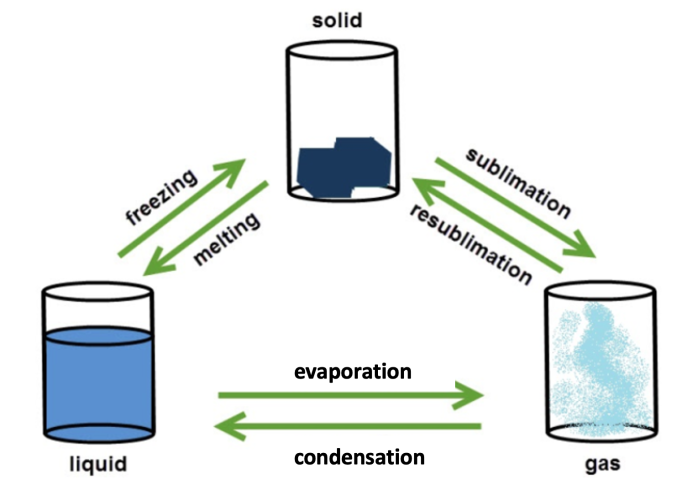
When heated, particles in a substance absorb energy from their surroundings. This means that they can move around more and much faster and when they gain enough energy, they can move further apart and eventually change state.
The opposite happens when a substance is cooled. The particles transfer some of their energy to the surroundings and become slower and closer together. You can see this in the diagram above - the particles in the gas are far apart and free to move independently of each other. As the gas cools to a liquid, the particles get closer together, and in a solid the particles are held together by strong forces of attraction. This is why particles in a solid can't move much, they can only vibrate on the spot.
There are some important words in the diagram above that you'll need to remember about state changes.
Freezing and condensing are the words we use to describe changes of state when energy is released to the surroundings - we call them exothermic.
Evaporating (or boiling), melting and subliming are the words we use to describe changes of state when energy is absorbed from the surroundings - we call them endothermic.
Finding it hard to remember these words?
Well exo sounds like 'exit', so you can remember that in exothermic processes, energy is leaving or 'exiting' the chemicals to go to the surroundings.
Endo sounds like 'into', so you can remember that endothermic processes involve energy going into the chemicals from the surroundings. Got it?
Temperature determines whether a substance will be in the solid, liquid or gaseous state, and at what point it will change state.
All substances have a melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. At a temperature above the melting point, the substance will be a liquid, at a temperature below the melting point, the substance will be a solid. So you could also call it the freezing point!
Substances also have a boiling point - the temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas. At a temperature above the boiling point, a substance will be a gas. At a temperature below the boiling point, it will be a liquid.
Woah, that's a lot of information! Take your time and read through this page again if you need to. When it starts to make sense, give some questions a go!








