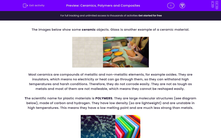
The images below show some ceramic objects. Glass is another example of a ceramic material.
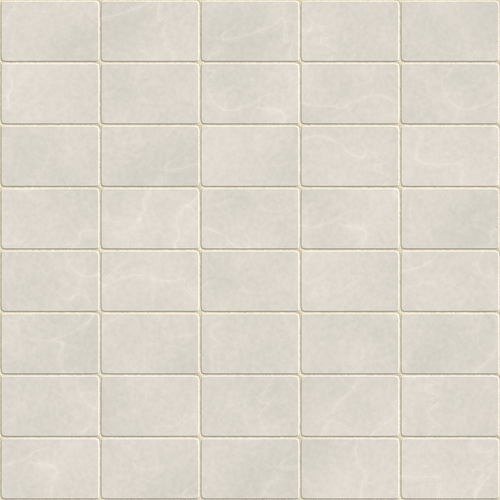


Most ceramics are compounds of metallic and non-metallic elements, for example oxides. They are insulators, which means no electricity or heat can go through them, so they can withstand high temperatures and harsh conditions. Therefore, they do not corrode easily. They are not as tough as metals and most of them are not malleable, which means they cannot be reshaped easily.
The scientific name for plastic materials is polymers. They are large molecular structures (see diagram below), made of carbon and hydrogen. They have low density (so are lightweight) and are unstable in high temperatures. This means they have a low melting point and are much less strong than metals.
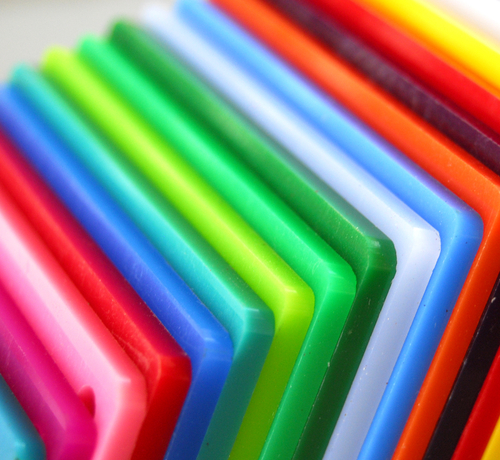


Polymers can be easily formed into different shapes and the cost of manufacture is relatively low. The properties of polymers make them the preferred material for many applications.
Composites are made of two or more materials with different properties. The different materials keep their properties as they are not merged with each other, but the combination of their properties makes them really useful. For example, fibreglass is a composite of a polymer and glass. Concrete is another example of a composite material, made of gravel, cement mixed with water.
That's lots of different facts to remember!
You can look back at the introduction at any point during this activity by clicking on the red Help button on the screen.
Let's get started!