In this activity, we are using what we know about Pythagoras' Theorem to calculate the length of a line on a graph.
In any right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
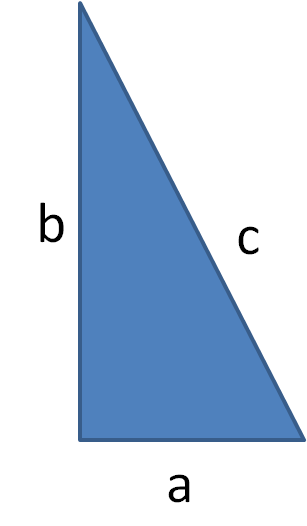
a2 + b2 = c2
Remember that the triangle must be right-angled and the hypotenuse is always the longest side and opposite the right angle.
Let's look at a typical question.
Example
What is the shortest distance between the two given points?
Answer
First, we draw a line to join the two points and then draw a vertical and horizontal line to form a right-angled triangle.
We can find the lengths of the shorter sides by counting the squares.
Now, we can use Pythagoras' Theorem to find the line length (the hypotenuse).
c2 = 32 + 42
c2 = 9 + 16
c2 = 25
c = √25
c = 5 units
Let's try some questions like this.







